Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage
- PMID: 16183841
- PMCID: PMC1255998
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.105.065961
Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage
Abstract
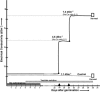
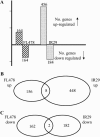
Rice (Oryza sativa), a salt-sensitive species, has considerable genetic variation for salt tolerance within the cultivated gene pool. Two indica rice genotypes, FL478, a recombinant inbred line derived from a population developed for salinity tolerance studies, and IR29, the sensitive parent of the population, were selected for this study. We used the Affymetrix rice genome array containing 55,515 probe sets to explore the transcriptome of the salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive genotypes under control and salinity-stressed conditions during vegetative growth. Response of the sensitive genotype IR29 is characterized by induction of a relatively large number of probe sets compared to tolerant FL478. Salinity stress induced a number of genes involved in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in IR29 but not in FL478. Cell wall-related genes were responsive in both genotypes, suggesting cell wall restructuring is a general adaptive mechanism during salinity stress, although the two genotypes also had some differences. Additionally, the expression of genes mapping to the Saltol region of chromosome 1 were examined in both genotypes. Single-feature polymorphism analysis of expression data revealed that IR29 was the source of the Saltol region in FL478, contrary to expectation. This study provides a genome-wide transcriptional analysis of two well-characterized, genetically related rice genotypes differing in salinity tolerance during a gradually imposed salinity stress under greenhouse conditions.
Figures

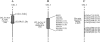
References
-
- Albinsky D, Masson JE, Bogucki A, Afsar K, Vass I, Nagy F, Paszkowski J (1999) Plant responses to genotoxic stress are linked to an ABA/salinity signaling pathway. Plant J 17: 73–82
-
- Baluska F, Samaj J, Menzel D (2003) Polar transport of auxin: carrier-mediated flux across the plasma membrane or neurotransmitter-like secretion? Trends Cell Biol 13: 282–285 - PubMed
-
- Bonilla P, Dvorak J, Mackill D, Deal K, Gregorio G (2002) RFLP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Philippine J Agric Sci 85: 68–76
-
- Cao Y, Ward JM, Kelly WB, Ichida AM, Gaber RF, Anderson JA, Uozumi N, Schroeder JI, Crawford NM (1995) Multiple genes, tissue specificity and expression-dependent modulation contribute to the functional diversity of potassium channels in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 109: 1093–1106 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carpita NC (1996) Structure and biogenesis of the cell walls in grasses. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47: 445–476 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

