Arginase I in myeloid suppressor cells is induced by COX-2 in lung carcinoma
- PMID: 16186186
- PMCID: PMC2213169
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20050715
Arginase I in myeloid suppressor cells is induced by COX-2 in lung carcinoma
Abstract
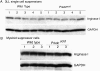
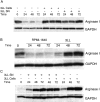
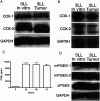
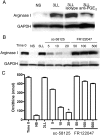
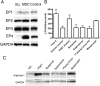
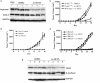
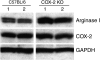
Myeloid suppressor cells (MSCs) producing high levels of arginase I block T cell function by depleting l-arginine in cancer, chronic infections, and trauma patients. In cancer, MSCs infiltrating tumors and in circulation are an important mechanism for tumor evasion and impair the therapeutic potential of cancer immunotherapies. However, the mechanisms that induce arginase I in MSCs in cancer are unknown. Using the 3LL mouse lung carcinoma, we aimed to characterize these mechanisms. Arginase I expression was independent of T cell-produced cytokines. Instead, tumor-derived soluble factors resistant to proteases induced and maintained arginase I expression in MSCs. 3LL tumor cells constitutively express cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 and produce high levels of PGE2. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of COX-2, but not COX-1, blocked arginase I induction in vitro and in vivo. Signaling through the PGE2 receptor E-prostanoid 4 expressed in MSCs induced arginase I. Furthermore, blocking arginase I expression using COX-2 inhibitors elicited a lymphocyte-mediated antitumor response. These results demonstrate a new pathway of prostaglandin-induced immune dysfunction and provide a novel mechanism that can help explain the cancer prevention effects of COX-2 inhibitors. Furthermore, an addition of arginase I represents a clinical approach to enhance the therapeutic potential of cancer immunotherapies.
Figures

References
-
- Gabrilovich, D.I., M.P. Velders, E.M. Sotomayor, and W.M. Kast. 2001. Mechanism of immune dysfunction in cancer mediated by immature Gr-1+ myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 166:5398–5406. - PubMed
-
- Bronte, V., P. Serafini, C. De Santo, I. Marigo, V. Tosello, A. Mazzoni, D.M. Segal, C. Staib, M. Lowel, G. Sutter, et al. 2003. IL-4-induced arginase 1 suppresses alloreactive T cells in tumor-bearing mice. J. Immunol. 170:270–278. - PubMed
-
- Liu, Y., J.A. Van Ginderachter, L. Brys, P. De Baetselier, G. Raes, and A.B. Geldhof. 2003. Nitric oxide-independent CTL suppression during tumor progression: association with arginase-producing (M2) myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 170:5064–5074. - PubMed
-
- Mazzoni, A., V. Bronte, A. Visintin, J.H. Spitzer, E. Apolloni, P. Serafini, P. Zanovello, and D.M. Segal. 2002. Myeloid suppressor lines inhibit T cell responses by an NO-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 168:689–695. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez, P.C., D.G. Quiceno, J. Zabaleta, B. Ortiz, A.H. Zea, M.B. Piazuelo, A. Delgado, P. Correa, J. Brayer, E.M. Sotomayor, et al. 2004. Arginase I production in the tumor microenvironment by mature myeloid cells inhibits T-cell receptor expression and antigen-specific T-cell responses. Cancer Res. 64:5839–5849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

