Hypercholesterolemia abrogates late preconditioning via a tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent mechanism in conscious rabbits
- PMID: 16186416
- PMCID: PMC3671759
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.566190
Hypercholesterolemia abrogates late preconditioning via a tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent mechanism in conscious rabbits
Abstract
Background: Although the late phase of ischemic preconditioning (PC) is known to confer cardioprotection in healthy animal models, it is unknown whether this phenomenon exists in the presence of hypercholesterolemia. The goal of this study was to determine whether the infarct-sparing effect of late PC is affected by hypercholesterolemia and, if so, whether a tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)-dependent mechanism is responsible for the loss of late PC.
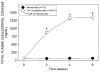
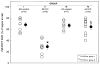
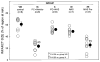
Methods and results: Conscious rabbits fed a normal diet or a 1% cholesterol diet for 6 weeks were subjected to ischemic PC (six 4-minute coronary occlusion/4-minute reperfusion cycles) and, 24 hours later, underwent a 30-minute occlusion followed by 3 days of reperfusion. A total of 125 rabbits were used. In normocholesterolemic rabbits, ischemic PC reduced infarct size, an effect that was abrogated by administration of the BH4 synthesis inhibitor N-acetylserotonin (15 mg/kg IV) before the 30-minute occlusion. In hypercholesterolemic rabbits, however, ischemic PC failed to reduce infarct size. Myocardial BH4 levels in the ischemic zone increased 24 hours after ischemic PC in normocholesterolemic rabbits but not in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. In addition, in normocholesterolemic rabbits, pretreatment with N-acetylserotonin completely abolished the ischemic PC-induced increase in myocardial BH4 levels.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that (1) hypercholesterolemia abrogates both the infarct-sparing effect of late PC and the concomitant upregulation of myocardial BH4, and (2) inhibition of myocardial BH4 synthesis in the absence of hypercholesterolemia is sufficient to abolish the infarct-sparing effect of late PC. The results support the concept that hypercholesterolemia abrogates late PC by preventing the upregulation of BH4, an essential cofactor for inducible nitric oxide synthase.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hypercholesterolemia blunts NO donor-induced late preconditioning against myocardial infarction in conscious rabbits.Basic Res Cardiol. 2004 Nov;99(6):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s00395-004-0485-4. Epub 2004 Sep 16. Basic Res Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15372283 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide donors induce late preconditioning against myocardial stunning and infarction in conscious rabbits via an antioxidant-sensitive mechanism.Circ Res. 1998 Jul 13;83(1):73-84. doi: 10.1161/01.res.83.1.73. Circ Res. 1998. PMID: 9670920 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide synthase is the mediator of late preconditioning against myocardial infarction in conscious rabbits.Circulation. 1998 Aug 4;98(5):441-9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.5.441. Circulation. 1998. PMID: 9714095
-
The early and late phases of ischemic preconditioning: a comparative analysis of their effects on infarct size, myocardial stunning, and arrhythmias in conscious pigs undergoing a 40-minute coronary occlusion.Circ Res. 1997 May;80(5):730-42. doi: 10.1161/01.res.80.5.730. Circ Res. 1997. PMID: 9130454
-
Cardioprotective function of inducible nitric oxide synthase and role of nitric oxide in myocardial ischemia and preconditioning: an overview of a decade of research.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001 Nov;33(11):1897-918. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.2001.1462. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001. PMID: 11708836 Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogen signaling and cardiovascular disease.Circ Res. 2011 Sep 2;109(6):687-96. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.236687. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21885836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ischemic preconditioning: Interruption of various disorders.J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2017 Apr;29(2):116-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jsha.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28373786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of pioglitazone on the abrogated cardioprotective effect of ischemic preconditioning in hyperlipidemic rat heart.Indian J Pharmacol. 2016 Jan-Feb;48(1):59-63. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.174545. Indian J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26997724 Free PMC article.
-
Preconditioning: a paradigm shift in the biology of myocardial ischemia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Jan;292(1):H19-27. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00712.2006. Epub 2006 Sep 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 16963615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The late phase of preconditioning and its natural clinical application--gene therapy.Heart Fail Rev. 2007 Dec;12(3-4):189-99. doi: 10.1007/s10741-007-9031-4. Heart Fail Rev. 2007. PMID: 17541820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bolli R. The late phase of preconditioning. Circ Res. 2000;87:972–983. - PubMed
-
- Bolli R, Bhatti ZA, Tang XL, Qiu Y, Zhang Q, Guo Y, Jadoon AK. Evidence that late preconditioning against myocardial stunning in conscious rabbits is triggered by the generation of nitric oxide. Circ Res. 1997;81:42–52. - PubMed
-
- Kuzuya T, Hoshida S, Yamashita N, Fuji H, Oe H, Hori M, Kamada T, Tada M. Delayed effects of sublethal ischemia on the acquisition of tolerance to ischemia. Circ Res. 1993;72:1293–1299. - PubMed
-
- Marber MS, Yellon DM. Myocardial adaptation, stress proteins, and the second window of protection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996;793:123–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-68088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-55757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-76794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-70897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL078825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-78825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-65660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL74351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

