A bacterial group II intron-encoded reverse transcriptase localizes to cellular poles
- PMID: 16186487
- PMCID: PMC1283441
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507057102
A bacterial group II intron-encoded reverse transcriptase localizes to cellular poles
Abstract
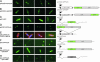
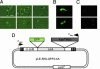
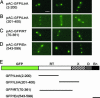
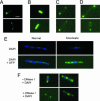
The Lactococcus lactis Ll.LtrB group II intron encodes a reverse transcriptase (LtrA protein) that binds the intron RNA to promote RNA splicing and intron mobility. Here, we used LtrA-GFP fusions and immunofluorescence microscopy to show that LtrA localizes to cellular poles in Escherichia coli and Lactococcus lactis. This polar localization occurs with or without coexpression of Ll.LtrB intron RNA, is observed over a wide range of cellular growth rates and expression levels, and is independent of replication origin function. The same localization pattern was found for three nonoverlapping LtrA subsegments, possibly reflecting dependence on common redundant signals and/or protein physical properties. When coexpressed in E. coli, LtrA interferes with the polar localization of the Shigella IcsA protein, which mediates polarized actin tail assembly, suggesting competition for a common localization determinant. The polar localization of LtrA could account for the preferential insertion of the Ll.LtrB intron in the origin and terminus regions of the E. coli chromosome, may facilitate access to exposed DNA in these regions, and could potentially link group II intron mobility to the host DNA replication and/or cell division machinery.
Figures



References
-
- Belfort, M., Derbyshire, V., Parker, M. M., Cousineau, B. & Lambowitz, A. M. (2002) in Mobile DNA II, eds. Craig, N. L., Craigie, R., Gellert, M. & Lambowitz, A. M. (Am. Soc. Microbiol., Washington, DC), pp. 761–783.
-
- Lambowitz, A. M. & Zimmerly, S. (2004) Annu. Rev. Genet. 38, 1–35. - PubMed
-
- Cui, X., Matsuura, M., Wang, Q., Ma, H. & Lambowitz, A. M. (2004) J. Mol. Biol. 340, 211–231. - PubMed
-
- San Filippo, J. & Lambowitz, A. M. (2002) J. Mol. Biol. 324, 933–951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

