Targeting angiogenesis: structural characterization and biological properties of a de novo engineered VEGF mimicking peptide
- PMID: 16186493
- PMCID: PMC1242306
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505047102
Targeting angiogenesis: structural characterization and biological properties of a de novo engineered VEGF mimicking peptide
Abstract
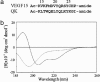
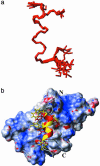
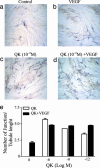
Modulating angiogenesis is an attractive goal because many pathological conditions depend on the growth of new vessels. Angiogenesis is mainly regulated by the VEGF, a mitogen specific for endothelial cells. In the last years, many efforts have been pursued to modulate the angiogenic response targeting VEGF and its receptors. Based on the x-ray structure of VEGF bound to the receptor, we designed a peptide, QK, reproducing a region of the VEGF binding interface: the helix region 17-25. NMR conformation analysis of QK revealed that it adopts a helical conformation in water, whereas the peptide corresponding to the alpha-helix region of VEGF, VEGF15, is unstructured. Biological assays in vitro and on bovine aorta endothelial cells suggested that QK binds to the VEGF receptors and competes with VEGF. VEGF15 did not bind to the receptors indicating that the helical structure is necessary for the biological activity. Furthermore, QK induced endothelial cells proliferation, activated cell signaling dependent on VEGF, and increased the VEGF biological response. QK promoted capillary formation and organization in an in vitro assay on matrigel. These results suggested that the helix region 17-25 of VEGF is involved in VEGF receptor activation. The peptide designed to resemble this region shares numerous biological properties of VEGF, thus suggesting that this region is of potential interest for biomedical applications, and molecules mimicking it could be attractive for therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo properties of the proangiogenic peptide QK.J Transl Med. 2009 Jun 8;7:41. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-41. J Transl Med. 2009. PMID: 19505323 Free PMC article.
-
VEGFR Recognition Interface of a Proangiogenic VEGF-Mimetic Peptide Determined In Vitro and in the Presence of Endothelial Cells by NMR Spectroscopy.Chemistry. 2018 Aug 6;24(44):11461-11466. doi: 10.1002/chem.201802117. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29799174
-
Characterization of a designed vascular endothelial growth factor receptor antagonist helical peptide with antiangiogenic activity in vivo.J Med Chem. 2011 Mar 10;54(5):1391-400. doi: 10.1021/jm101435r. Epub 2011 Jan 31. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21280635
-
Targeting tumor micro-environment for design and development of novel anti-angiogenic agents arresting tumor growth.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;113(2):333-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24139944 Review.
-
Peptides targeting angiogenesis related growth factor receptors.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(21):2414-29. doi: 10.2174/138161209788682235. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19601840 Review.
Cited by
-
Freeze-Casting with 3D-Printed Templates Creates Anisotropic Microchannels and Patterned Macrochannels within Biomimetic Nanofiber Aerogels for Rapid Cellular Infiltration.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Jun;10(12):e2100238. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202100238. Epub 2021 May 24. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 34029004 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in three-dimensional printing with growth factors.J Control Release. 2019 Feb 10;295:50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.12.035. Epub 2018 Dec 20. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 30579982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-assembling Molecular Medicine for the Subacute Phase of Ischemic Stroke.Neurochem Res. 2022 Sep;47(9):2488-2498. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03638-5. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35666393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tethering QK peptide to enhance angiogenesis in elastin-like recombinamer (ELR) hydrogels.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019 Feb 14;30(2):30. doi: 10.1007/s10856-019-6232-z. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019. PMID: 30762134
-
Comparing variable-length polyglutamate domains to anchor an osteoinductive collagen-mimetic peptide to diverse bone grafting materials.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014 Nov-Dec;29(6):1437-45. doi: 10.11607/jomi.3759. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014. PMID: 25397807 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

