Structure of the calcium-rich signature domain of human thrombospondin-2
- PMID: 16186819
- PMCID: PMC2219892
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb997
Structure of the calcium-rich signature domain of human thrombospondin-2
Abstract
Thrombospondins (THBSs) are secreted glycoproteins that have key roles in interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix. Here, we describe the 2.6-A-resolution crystal structure of the glycosylated signature domain of human THBS2, which includes three epidermal growth factor-like modules, 13 aspartate-rich repeats and a lectin-like module. These elements interact extensively to form three structural regions termed the stalk, wire and globe. The THBS2 signature domain is stabilized by these interactions and by a network of 30 bound Ca(2+) ions and 18 disulfide bonds. The structure suggests how genetic alterations of THBSs result in disease.
Figures



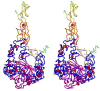


References
-
- Christopherson KS, et al. Thrombospondins are astrocyte-secreted proteins that promote CNS synaptogenesis. Cell. 2005;120 :421–33. - PubMed
-
- Kyriakides TR, et al. Megakaryocytes require thrombospondin-2 for normal platelet formation and function. Blood. 2003;101 :3915–23. - PubMed
-
- Adams JC, et al. Characterisation of Drosophila thrombospondin defines an early origin of pentameric thrombospondins. J Mol Biol. 2003;328 :479–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

