Receptor-activity-modifying proteins are required for forward trafficking of the calcium-sensing receptor to the plasma membrane
- PMID: 16188935
- PMCID: PMC3311923
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.02598
Receptor-activity-modifying proteins are required for forward trafficking of the calcium-sensing receptor to the plasma membrane
Abstract
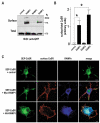
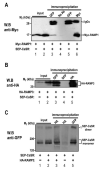
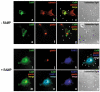
The calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a class III G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that responds to changes in extracellular calcium concentration and plays a crucial role in calcium homeostasis. The mechanisms controlling CaSR trafficking and surface expression are largely unknown. Using a CaSR tagged with the pH-sensitive GFP super-ecliptic pHluorin (SEP-CaSR), we show that delivery of the GPCR to the cell surface is dependent on receptor-activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs). We demonstrate that SEP-CaSRs are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in COS7 cells that do not contain endogenous RAMPs whereas they are delivered to the plasma membrane in HEK 293 cells that do express RAMP1. Coexpression of RAMP1 or RAMP3, but not RAMP2, in COS7 cells was sufficient to target the CaSR to the cell surface. RAMP1 and RAMP3 colocalised and coimmunoprecipitated with the CaSR suggesting that these proteins associate within the cell. Our results indicate that RAMP expression promotes the forward trafficking of the GPCR from the ER to the Golgi apparatus and results in mature CaSR glycosylation, which is not observed in RAMP-deficient cells. Finally, silencing of RAMP1 in the endogenously expressing HEK293 cells using siRNA resulted in altered CaSR traffic. Taken together, our results show that the association with RAMPs is necessary and sufficient to transfer the immature CaSR retained in the ER towards the Golgi where it becomes fully glycosylated prior to delivery to the plasma membrane and demonstrate a role for RAMPs in the trafficking of a class III GPCR.
Figures






References
-
- Ashby MC, Ibaraki K, Henley JM. It’s green outside: tracking cell surface proteins with pH-sensitive GFP. Trends Neurosci. 2004b;27:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Awata H, Huang C, Handlogten ME, Miller RT. Interaction of the calcium-sensing receptor and filamin, a potential scaffolding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:34871–34879. - PubMed
-
- Bai M, Trivedi S, Brown EM. Dimerization of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaR) on the cell surface of CaR-transfected HEK293 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:23605–23610. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

