Cathepsin L is involved in proteolytic processing of the Hendra virus fusion protein
- PMID: 16188974
- PMCID: PMC1235853
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.20.12714-12720.2005
Cathepsin L is involved in proteolytic processing of the Hendra virus fusion protein
Abstract
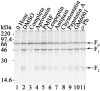
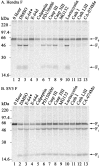
Proteolytic processing of paramyxovirus fusion (F) proteins is essential for the generation of a mature and fusogenic form of the F protein. Although many paramyxovirus F proteins are proteolytically processed by the cellular protease furin at a multibasic cleavage motif, cleavage of the newly emerged Hendra virus F protein occurs by a previously unidentified cellular protease following a single lysine at residue 109. We demonstrate here that the cellular protease cathepsin L is involved in converting the Hendra virus precursor F protein (F(0)) to the active F(1) + F(2) disulfide-linked heterodimer. To initially identify the class of protease involved in Hendra virus F protein cleavage, Vero cells transfected with pCAGGS-Hendra F or pCAGGS-SV5 F (known to be proteolytically processed by furin) were metabolically labeled and chased in the absence or presence of serine, cysteine, aspartyl, and metalloprotease inhibitors. Nonspecific and specific protease inhibitors known to decrease cathepsin activity inhibited proteolytic processing of Hendra virus F but had no effect on simian virus 5 F processing. We next designed shRNA oligonucleotides to cathepsin L which dramatically reduced cathepsin L protein expression and enzyme activity. Cathepsin L shRNA-expressing Vero cells transfected with pCAGGS-Hendra F demonstrated a nondetectable amount of cleavage of the Hendra virus F protein and significantly decreased membrane fusion activity. Additionally, we found that purified human cathepsin L processed immunopurified Hendra virus F(0) into F(1) and F(2) fragments. These studies introduce a novel mechanism for primary proteolytic processing of viral glycoproteins and also suggest a previously unreported biological role for cathepsin L.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subcellular localization and calcium and pH requirements for proteolytic processing of the Hendra virus fusion protein.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(17):9154-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9154-9163.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15308711 Free PMC article.
-
A mature and fusogenic form of the Nipah virus fusion protein requires proteolytic processing by cathepsin L.Virology. 2006 Mar 15;346(2):251-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.01.007. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16460775 Free PMC article.
-
Surface density of the Hendra G protein modulates Hendra F protein-promoted membrane fusion: role for Hendra G protein trafficking and degradation.Virology. 2007 Jul 5;363(2):419-29. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.01.029. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17328935 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin L and Arg/Lys aminopeptidase: a distinct prohormone processing pathway for the biosynthesis of peptide neurotransmitters and hormones.Biol Chem. 2004 Jun;385(6):473-80. doi: 10.1515/BC.2004.055. Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15255178 Review.
-
Cathepsins as transcriptional activators?Dev Cell. 2004 May;6(5):610-1. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(04)00141-8. Dev Cell. 2004. PMID: 15130484 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of sequence and structure of the Hendra fusion protein fusion peptide in membrane fusion.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 24;287(35):30035-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.367862. Epub 2012 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22761418 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin W Is Required for Escape of Influenza A Virus from Late Endosomes.mBio. 2015 Jun 9;6(3):e00297. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00297-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26060270 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 (BPIV3) Enters HeLa Cells via Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis in a Cholesterol- and Dynamin-Dependent Manner.Viruses. 2021 May 31;13(6):1035. doi: 10.3390/v13061035. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34072688 Free PMC article.
-
Nipah virus fusion protein: influence of cleavage site mutations on the cleavability by cathepsin L, trypsin and furin.Virus Res. 2009 Nov;145(2):300-6. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.07.020. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Virus Res. 2009. PMID: 19665506 Free PMC article.
-
A functional henipavirus envelope glycoprotein pseudotyped lentivirus assay system.Virol J. 2010 Nov 12;7:312. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-312. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 21073718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bossart, K. N., L.-F. Wang, B. Eaton, and C. C. Broder. 2001. Functional expression and membrane fusion tropism of the envelope glycoproteins of Hendra virus. Virology 290:121-135. - PubMed
-
- Buchholz, U. J., S. Finke, and K.-K. Conzelmann. 1999. Generation of bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) from cDNA: BRSV NS2 is not essential for virus replication in tissue culture, and the human RSV leader region acts as a functional BRSV genome promoter. J. Virol. 73:251-259. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chua, K. B., W. J. Bellini, P. A. Rota, B. H. Harcourt, A. Tamin, S. K. Lam, T. G. Ksiazek, P. E. Rollin, S. R. Zaki, W. Shieh, C. S. Goldsmith, D. J. Gubler, J. T. Roehrig, B. Eaton, A. R. Gould, J. Olson, H. Field, P. Daniels, A. E. Ling, C. J. Peters, L. J. Anderson, and B. W. Mahy. 2000. Nipah virus: a recently emergent deadly paramyxovirus. Science 288:1432-1435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

