Dominantly inherited beta thalassaemia intermedia caused by a new single nucleotide deletion in exon 2 of the beta globin gene: Hb morgantown (beta91 CTG>CG)
- PMID: 16189162
- PMCID: PMC1770750
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2004.023010
Dominantly inherited beta thalassaemia intermedia caused by a new single nucleotide deletion in exon 2 of the beta globin gene: Hb morgantown (beta91 CTG>CG)
Abstract
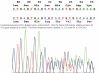
Family members in multiple generations of an Irish-American family were investigated for moderate to severe microcytic anaemia, inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. A novel frameshift mutation of the beta globin gene was discovered. This study highlights the importance of considering dominantly inherited beta thalassemia in the investigation of anaemia, even in patients with ethnic backgrounds not usually associated with beta thalassaemia.
Figures

References
-
- Olivieri NF. The β-thalassemias. N Engl J Med 1999;341:99–109. - PubMed
-
- Thein SL. Dominant β thalassaemia: molecular basis and pathophysiology. Br J Haematol 1992;80:273–7. - PubMed
-
- Thein SL. Is it dominantly inherited β thalassaemia or just a β-chain variant that is highly unstable? Br J Haematol 1999;107:12–21. - PubMed
-
- Stamatoyannopoulos G, Woodson R, Papayannopoulou T, et al. Inclusion-body β-thalassemia trait. A form of β thalassemia producing clinical manifestations in simple heterozygotes. N Engl J Med 1974;290:939–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
