Loading of hydrophobic materials into polymer particles: implications for fluorescent nanosensors and drug delivery
- PMID: 16190679
- PMCID: PMC5359015
- DOI: 10.1021/ja052188y
Loading of hydrophobic materials into polymer particles: implications for fluorescent nanosensors and drug delivery
Abstract
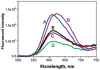
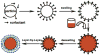
A straightforward method for loading hydrophobic materials into commercially available polymer nano- or microparticles is described. PMMA and PS nano/microparticles were swelled by an organic solvent with an ionic surfactant (SDS) to stabilize the particles in aqueous solution. FITC and Ru(dpp)3Cl2 were loaded into those particles based on the principle of "like dissolves like". Further surface modification of the loaded particles was achieved via layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly. Culture of fibroblasts with the dye-doped, coated particles showed that the cells internalized the fluorescent particles with no apparent toxic effects. The findings suggest the facile process could be useful in a wide range of applications for fluorescent micro/nanosensors and drug delivery.
Figures


References
-
- Roy I, Ohulchanskyy TY, Pudavar HE, Bergey EJ, Oseroff AR, Morgan J, Dougherty TJ, Prasad PN. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:7860–7865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

