Acute gamma-secretase inhibition improves contextual fear conditioning in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 16192379
- PMCID: PMC6725598
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2693-05.2005
Acute gamma-secretase inhibition improves contextual fear conditioning in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
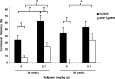
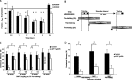
Transgenic mice (Tg2576) overexpressing the Swedish mutation of the human amyloid precursor protein display biochemical, pathological, and behavioral markers consistent with many aspects of Alzheimer's disease, including impaired hippocampal function. Impaired, hippocampal-dependent, contextual fear conditioning (CFC) is observed in mice as young as 20 weeks of age. This impairment can be attenuated after treatment before training with the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.). A rolipram-associated improvement is also observed in the littermate controls, suggesting that the effect of rolipram is independent of beta-amyloid. Acute treatment before training (but not after training or before testing) with the gamma-secretase inhibitor (GSI) N-[N-(3,5-difluorophenacetyl)-l-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine-t-butylester (DAPT), at a dose that reduces brain concentrations of beta-amyloid (100 mg/kg), attenuates the impairment in 20- to 65-week-old Tg2576 mice. Importantly, DAPT had no effect on performance of control littermates. These data are supportive of a role of beta-amyloid in the impairment of CFC in Tg2576 mice. Furthermore, they suggest that acute treatment with GSI may provide improved cognitive functioning as well as disease-modifying effects in Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

References
-
- Berg L, McKeell Jr DW, Miller JP, Storandt M, Rubin EH, Morris JC, Baty J, Coats M, Norton J, Goate AM, Price JL, Gearing M, Mirra SS, Saunders AM (1998) Clinicopathologic studies in cognitively healthy aging and Alzheimer disease: relation of histologic markers to dementia severity, age, sex, and apolipoprotein E genotype. Arch Neurol 55: 326–335. - PubMed
-
- Chapman PF, White GL, Jones MW, Cooper-Blacketer D, Marshall VJ, Irizarry M, Younkin L, Good MA, Bliss TVP, Hyman BT, Younkin SG, Hsiao KK (1999) Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nat Neurosci 2: 271–276. - PubMed
-
- Cleary JP, Walsh DM, Hofmeister JJ, Shankar GM, Kuskowski MA, Selkoe DJ, Ashe KH (2005) Natural oligomers of the amyloid-β protein specifically disrupt cognitive function. Nat Neurosci 8: 79–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
