Hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling mediates the anti-fibrotic action of 9-cis-retinoic acid in glomerular mesangial cells
- PMID: 16192631
- PMCID: PMC1603682
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61185-6
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling mediates the anti-fibrotic action of 9-cis-retinoic acid in glomerular mesangial cells
Abstract
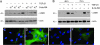
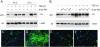
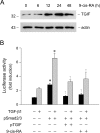
Retinoic acid (RA), an active metabolite of vitamin A, plays a critical role in the regulation of cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. RA action is primarily mediated through its receptors, ligand-dependent transcription factors of the steroid/thyroid/vitamin D nuclear receptor superfamily. Recent studies indicate that administration of RA mitigates progressive kidney disease, underscoring its renoprotective potential. In this study, we investigated the effects of 9-cis-RA on glomerular mesangial cell activation induced by transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 using an in vitro cell culture system. In human mesangial cells 9-cis-RA suppressed TGF-beta1-induced alpha-smooth muscle actin, fibronectin, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression, but it did not significantly affect cell proliferation and survival. Interestingly, 9-cis-RA induced hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) mRNA expression and protein secretion, stimulated HGF promoter activity, and activated c-met receptor phosphorylation. Similar to HGF, 9-cis-RA induced expression of the Smad transcriptional co-repressor TGIF in mesangial cells. Overexpression of exogenous TGIF by transfection or 9-cis-RA treatment suppressed trans-activation of the TGF-beta-responsive promoter. Moreover, conditional ablation of the c-met receptor completely abolished the anti-fibrotic effect of 9-cis-RA and abrogated TGIF induction. Collectively, these results indicate that 9-cis-RA possesses anti-fibrotic ability by antagonizing TGF-beta1 in mesangial cells and that 9-cis-RA activity is likely mediated through a mechanism dependent on HGF/c-met receptor signaling.
Figures
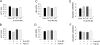

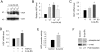

References
-
- Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
-
- Wagner J. Potential role of retinoids in the therapy of renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16:441–444. - PubMed
-
- Xu Q, Lucio Cazana J, Kitamura M, Ruan X, Fine LG, Norman JT. Retinoids in nephrology: promise and pitfalls. Kidney Int. 2004;66:2119–2131. - PubMed
-
- Zhou XF, Shen XQ, Shemshedini L. Ligand-activated retinoic acid receptor inhibits AP-1 transactivation by disrupting c-Jun/c-Fos dimerization. Mol Endocrinol. 1999;13:276–285. - PubMed
-
- Na SY, Kang BY, Chung SW, Han SJ, Ma X, Trinchieri G, Im SY, Lee JW, Kim TS. Retinoids inhibit interleukin-12 production in macrophages through physical associations of retinoid X receptor and NFkappaB. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:7674–7680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

