Calotropis procera latex-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia--effect of antiinflammatory drugs
- PMID: 16192671
- PMCID: PMC1526484
- DOI: 10.1155/MI.2005.216
Calotropis procera latex-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia--effect of antiinflammatory drugs
Abstract
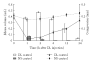
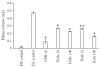
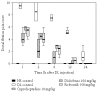
The milky white latex of plant Calotropis procera produces inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes on accidental exposure. It produces edema on local administration due to the release of histamine and prostaglandins and is associated with hyperalgesia. In the present study we have evaluated the antiedematous and analgesic activity of antiinflammatory drugs against inflammatory response induced by dried latex (DL) of C procera in rat paw edema model. An aqueous extract of DL of C procera was injected into the subplantar surface of the rat paw and the paw volume was measured by a plethysmometer at 0, 1, 2, 6, 12, and 24 hours. Concomitantly the hyperalgesic response was also evaluated by motility test, stair climbing ability test, dorsal flexion pain test, compression test, and observing the grooming behavior. The inhibitory effect of diclofenac and rofecoxib on edema formation and hyperalgesic response was compared with cyproheptadine (CPH). DL-induced edema formation was maximum at 2 hours that was associated with decreased pain threshold, functional impairment, and grooming. Treatment with antiinflammatory drugs and CPH significantly attenuated the edematous response and grooming, increased the pain threshold, and improved functional parameters. Both antiinflammatory and antiserotonergic drugs significantly inhibited the hyperalgesia associated with DL-induced paw edema. Rofecoxib was found to be superior than diclofenac and was as effective as CPH in ameliorating the hyperalgesia. However, it was found to be less effective than CPH in attenuating edema formation.
Figures
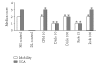
References
-
- CSIR Publication and Information Directorate. Wealth of India: Raw materials. III. New Delhi, India: CSIR Publication and Information Directorate; 1992. pp. 78–84.
-
- Mahmoud OM, Adam SE, Tartour G. The effects of Calotropis procera on small ruminants II. Effects of administration of the latex to sheep and goats. J Comp Pathol. 1979;89(2):251–263. - PubMed
-
- Kumar VL, Arya S. Medicinal uses and pharmacological properties of Calotropis procera . Recent Prog Med Plants. (in Press).
-
- Majumder PK, Kumar VL. Anti-inflammatory activity of fractions of latex of Calotropis procera in carrageenin induced paw oedema. Phytother Res. 1997;11:166–167.
-
- Dewan S, Sangraula H, Kumar VL. Preliminary studies on the analgesic activity of the latex of Calotropis procera. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;73(1-2):307–311. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

