SOX7 and SOX18 are essential for cardiogenesis in Xenopus
- PMID: 16193513
- PMCID: PMC1473172
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.20565
SOX7 and SOX18 are essential for cardiogenesis in Xenopus
Abstract
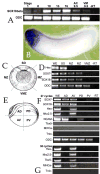
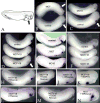
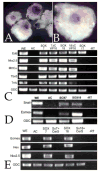
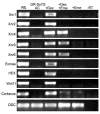
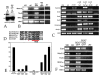
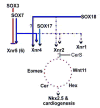
Early in vertebrate development, endodermal signals act on mesoderm to induce cardiogenesis. The F-type SOXs SOX7 and SOX18beta are expressed in the cardiogenic region of the early Xenopus embryo. Injection of RNAs encoding SOX7 or SOX18beta, but not the related F-type SOX, SOX17, leads to the nodal-dependent expression of markers of cardiogenesis in animal cap explants. Injection of morpholinos directed against either SOX7 or SOX18mRNAs lead to a partial inhibition of cardiogenesis in vivo, while co-injection of SOX7 and SOX18 morpholinos strongly inhibited cardiogenesis. SOX7 RNA rescued the effects of the SOX18 morpholino and visa versa, indicating that the proteins have redundant functions. In animal cap explants, it appears that SOX7 and SOX18 act indirectly through Xnr2 to induce mesodermal (Eomesodermin, Snail, Wnt11), organizer (Cerberus) and endodermal (endodermin, Hex) tissues, which then interact to initiate cardiogenesis. Versions of SOX7 and SOX18 with their C-terminal, beta-catenin interaction domains replaced by a transcriptional activator domain failed to antagonize beta-catenin activation of Siamois, but still induced cardiogenesis. These observations identify SOX7 and SOX18 as important, and previously unsuspected, regulators of cardiogenesis in Xenopus.
Copyright 2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SOX7 is an immediate-early target of VegT and regulates Nodal-related gene expression in Xenopus.Dev Biol. 2005 Feb 15;278(2):526-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.11.008. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15680368
-
Repression of nodal expression by maternal B1-type SOXs regulates germ layer formation in Xenopus and zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2004 Sep 1;273(1):23-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.05.019. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15302595
-
Multiple functions of Cerberus cooperate to induce heart downstream of Nodal.Dev Biol. 2007 Mar 1;303(1):57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.10.033. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17123501 Free PMC article.
-
SOX18 and the transcriptional regulation of blood vessel development.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2001 Nov;11(8):318-24. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(01)00131-1. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2001. PMID: 11728880 Review.
-
SOXF transcription factors in cardiovascular development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar;63:50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.07.021. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27470491 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential expression pattern of the human endoderm-specific transcription factor sox17 in various tissues and cells.Int J Organ Transplant Med. 2012;3(4):183-7. Int J Organ Transplant Med. 2012. PMID: 25013644 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor SOX18 regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and guidance molecules in human endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030982. Epub 2012 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22292085 Free PMC article.
-
SOX7 loss-of-function variation as a cause of familial congenital heart disease.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Mar 15;14(3):1672-1684. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35422912 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SOX18 as a New Gene Predisposing to Congenital Heart Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Aug 8;12(8):1917. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12081917. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010266 Free PMC article.
-
Chibby functions in Xenopus ciliary assembly, embryonic development, and the regulation of gene expression.Dev Biol. 2014 Nov 15;395(2):287-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25220153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ariizumi T, Kinoshita M, Yokota C, Takano K, Fukuda K, Moriyama N, Malacinski GM, Asashima M. Amphibian in vitro heart induction: a simple and reliable model for the study of vertebrate cardiac development. Int J Dev Biol. 2003;47:405–10. - PubMed
-
- Aybar MJ, Nieto MA, Mayor R. Snail precedes slug in the genetic cascade required for the specification and migration of the Xenopus neural crest. Development. 2003;130:483–94. - PubMed
-
- Bouwmeester T, Kim S, Sasai Y, Lu B, De Robertis EM. Cerberus is a head-inducing secreted factor expressed in the anterior endoderm of Spemann’s organizer. Nature. 1996;382:595–601. - PubMed
-
- Brannon M, Kimelman D. Activation of Siamois by the Wnt pathway. Dev Biol. 1996;180:344–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

