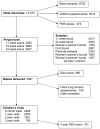
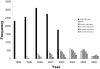
Cohort profile: The Southampton Women's Survey
- PMID: 16195252
- PMCID: PMC4579566
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyi202
Cohort profile: The Southampton Women's Survey
Figures

References
-
- Barker DJP. Mother, babies and health in later life. Churchill Livingstone; Edinburgh: 1998.
-
- Gluckman P, Hanson M. The fetal matrix. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2005.
-
- Godfrey KM. The “Developmental Origins” hypothesis: epidemiology. In: Hanson MA, Gluckman PD, editors. Developmental Origins of Health and Disease – a Biomedical Perspective. Cambridge University Press; 2005. in press.
-
- Robinson S, Godfrey K, Osmond C, Cox V, Barker D. Evaluation of a food frequency questionnaire used to assess nutrient intakes in pregnant women. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1996;50:302–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

