Hairless triggers reactivation of hair growth by promoting Wnt signaling
- PMID: 16195376
- PMCID: PMC1253615
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507609102
Hairless triggers reactivation of hair growth by promoting Wnt signaling
Abstract
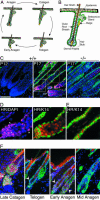
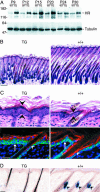
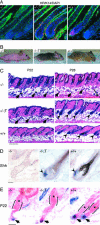
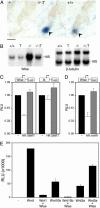
The mammalian hair cycle involves periodic regeneration of a tiny organ, the hair follicle, through a stem-cell-mediated process. The Hairless (Hr) gene encodes a nuclear receptor corepressor (HR) that is essential for hair follicle regeneration, but its role in this process is unknown. Here, we demonstrate that transgenic expression of HR in progenitor keratinocytes rescues follicle regeneration in Hr(-/-) mice. We show that expression of Wise, a modulator of Wnt signaling, is repressed by HR in these cells, coincident with the timing of follicle regeneration. This work links HR and Wnt function, providing a model in which HR regulates the precise timing of Wnt signaling required for hair follicle regeneration.
Figures

References
-
- Hardy, M. H. (1992) Trends Genet. 8, 55-61. - PubMed
-
- Oshima, H., Rochat, A., Kedzia, C., Kobayashi, K. & Barrandon, Y. (2001) Cell 104, 233-245. - PubMed
-
- Cotsarelis, G., Sun, T. T. & Lavker, R. M. (1990) Cell 61, 1329-1337. - PubMed
-
- Taylor, G., Lehrer, M. S., Jensen, P. J., Sun, T. T. & Lavker, R. M. (2000) Cell 102, 451-461. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, L. & Fuchs, E. (2003) Genes Dev. 17, 1189-1200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

