Histone H3 tail positioning and acetylation by the c-Myb but not the v-Myb DNA-binding SANT domain
- PMID: 16195416
- PMCID: PMC1257399
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.355405
Histone H3 tail positioning and acetylation by the c-Myb but not the v-Myb DNA-binding SANT domain
Abstract
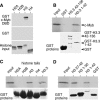
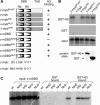
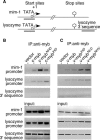
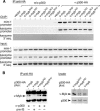
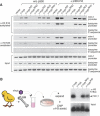
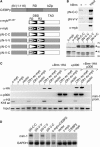
The c-Myb transcription factor coordinates proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic precursor cells. Myb has three consecutive N-terminal SANT-type repeat domains (R1, R2, R3), two of which (R2, R3) form the DNA-binding domain (DBD). Three amino acid substitutions in R2 alter the way Myb regulates genes and determine the leukemogenicity of the retrovirally transduced v-Myb oncogene. The molecular mechanism of how these mutations unleash the leukemogenic potential of Myb is unknown. Here we demonstrate that the c-Myb-DBD binds to the N-terminal histone tails of H3 and H3.3. C-Myb binding facilitates histone tail acetylation, which is mandatory during activation of prevalent differentiation genes in conjunction with CCAAT enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP). Leukemogenic mutations in v-Myb eliminate the interaction with H3 and acetylation of H3 tails and abolish activation of endogenous differentiation genes. In primary v-myb-transformed myeloblasts, pharmacologic enhancement of H3 acetylation restored activation of differentiation genes and induced cell differentiation. Our data link a novel chromatin function of c-Myb with lineage-specific expression of differentiation genes and relate the loss of this function with the leukemic conversion of Myb.
Figures

References
-
- Aasland R., Stewart, A.F., and Gibson, T. 1996. The SANT domain: A putative DNA-binding domain in the SWI-SNF and ADA complexes, the transcriptional co-repressor N-CoR and TFIIIB. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21: 87-88. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A.S., Bindels, P.C., Xu, J., Miedema, K., Kremer, H., and Hennig, W. 1995. Structure and expression of histone H3.3 genes in Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila hydei. Genome 38: 586-600. - PubMed
-
- Ansieau S. and Leutz, A. 2002. The conserved Mynd domain of BS69 binds cellular and oncoviral proteins through a common PXLXP motif. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 4906-4910. - PubMed
-
- Beall E.L., Manak, J.R., Zhou, S., Bell, M., Lipsick, J.S., and Botchan, M.R. 2002. Role for a Drosophila Myb-containing protein complex in site-specific DNA replication. Nature 420: 833-837. - PubMed
-
- Boyer L.A., Langer, M.R., Crowley, K.A., Tan, S., Denu, J.M., and Peterson, C.L. 2002. Essential role for the SANT domain in the functioning of multiple chromatin remodeling enzymes. Mol. Cell 10: 935-942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
