Recruitment of the Sonic hedgehog signalling cascade in electroconvulsive seizure-mediated regulation of adult rat hippocampal neurogenesis
- PMID: 16197497
- PMCID: PMC4820647
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04317.x
Recruitment of the Sonic hedgehog signalling cascade in electroconvulsive seizure-mediated regulation of adult rat hippocampal neurogenesis
Abstract
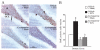
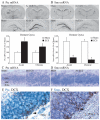
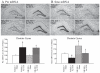
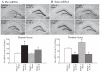
Electroconvulsive seizure (ECS) induces structural remodelling in the adult mammalian brain, including an increase in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. The molecular mechanisms that underlie this increase in the proliferation of adult hippocampal progenitors are at present not well understood. We hypothesized that ECS may recruit the Sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway to mediate its effects on adult hippocampal neurogenesis, as Shh is known to enhance the proliferation of neuronal progenitors and is expressed in the adult basal forebrain, a region that sends robust projections to the hippocampus. Here we demonstrate that the ECS-induced increase in proliferation of adult hippocampal progenitors was completely blocked in animals treated with cyclopamine, a pharmacological inhibitor of Shh signalling. Our results suggest that both acute and chronic ECS enhance Shh signalling in the adult hippocampus, as we observed a robust upregulation of Patched (Ptc) mRNA, a component of the Shh receptor complex and a downstream transcriptional target of Shh signalling. This increase was rapid and restricted to the dentate gyrus, where the adult hippocampal progenitors reside. In addition, both acute and chronic ECS decreased Smoothened (Smo) mRNA, the other component of the Shh receptor complex, selectively within the dentate gyrus. However, ECS did not appear to influence Shh expression within the basal forebrain, the site from which it has been suggested to be anterogradely transported to the hippocampus. Together, our findings demonstrate that ECS regulates the Shh signalling cascade and indicate that the Shh pathway may be an important mechanism through which ECS enhances adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
Figures
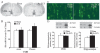
References
-
- Alcedo J, Zou Y, Noll N. Posttranscriptional regulation of smoothened is part of a selfcorrecting mechanism in the Hedgehog signaling system. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:457–465. - PubMed
-
- Bennin DA, Don AS, Brake T, McKenzie JL, Rosenbaum H, Ortiz L, DePaoli-Roah AA, Horne MC. Cyclin G2 associates with protein phosphatase 2A catalytic and regulatory B subunits in active complexes and induces nuclear aberrations and a G1/S phase cell cycle arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:27449–27467. - PubMed
-
- Bergstein I, Leopold PL, Sato N, Panteleyev AA, Christiano AM, Crystal RG. In vivo enhanced expression of Patched dampens the Sonic hedgehog pathway. Mol. Ther. 2002;6:258–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

