Cnu, a novel oriC-binding protein of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 16199570
- PMCID: PMC1251610
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.20.6998-7008.2005
Cnu, a novel oriC-binding protein of Escherichia coli
Abstract
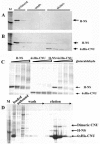
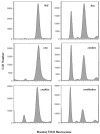
We have found, using a newly developed genetic method, a protein (named Cnu, for oriC-binding nucleoid-associated) that binds to a specific 26-base-pair sequence (named cnb) in the origin of replication of Escherichia coli, oriC. Cnu is composed of 71 amino acids (8.4 kDa) and shows extensive amino acid identity to a group of proteins belonging to the Hha/YmoA family. Cnu was previously discovered as a protein that, like Hha, complexes with H-NS in vitro. Our in vivo and in vitro assays confirm the results and further suggest that the complex formation with H-NS is involved in Cnu/Hha binding to cnb. Unlike the hns mutants, elimination of either the cnu or hha gene did not disturb the growth rate, origin content, and synchrony of DNA replication initiation of the mutants compared to the wild-type cells. However, the cnu hha double mutant was moderately reduced in origin content. The Cnu/Hha complex with H-NS thus could play a role in optimal activity of oriC.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structure of the nucleoid-associated protein Cnu reveals common binding sites for H-NS in Cnu and Hha.Biochemistry. 2008 Feb 19;47(7):1993-2001. doi: 10.1021/bi701914t. Epub 2008 Jan 12. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18189420
-
YdgT, the Hha paralogue in Escherichia coli, forms heteromeric complexes with H-NS and StpA.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Oct;54(1):251-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04268.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15458420
-
N9L and L9N mutations toggle Hha binding and hemolysin regulation by Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae H-NS.FEBS Lett. 2009 Sep 3;583(17):2911-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.07.054. Epub 2009 Aug 4. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19660457
-
The novel Hha/YmoA family of nucleoid-associated proteins: use of structural mimicry to modulate the activity of the H-NS family of proteins.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Jan;63(1):7-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05497.x. Epub 2006 Nov 14. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17116239 Review.
-
Role of the Hha/YmoA family of proteins in the thermoregulation of the expression of virulence factors.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Feb;291(6-7):425-32. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00149. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11890540 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary and functional divergence of Sfx, a plasmid-encoded H-NS homolog, underlies the regulation of IncX plasmid conjugation.mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0208924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02089-24. Epub 2024 Dec 23. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39714162 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple DNA Binding Proteins Contribute to Timing of Chromosome Replication in E. coli.Front Mol Biosci. 2016 Jun 28;3:29. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00029. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27446932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YmoA functions as a molecular stress sensor in Yersinia.Commun Biol. 2025 Feb 13;8(1):225. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07675-y. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39948215 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in nucleoid morphology and origin localization upon inhibition or alteration of the actin homolog, MreB, of Vibrio cholerae.J Bacteriol. 2007 Oct;189(20):7450-63. doi: 10.1128/JB.00362-07. Epub 2007 Aug 17. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17704222 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Individual SeqA Binding Sites of the E. coli Origin Reveals Robustness of Replication Initiation Synchrony.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 8;11(12):e0166722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166722. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27930658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barik, S., and M. S. Galinski. 1991. “Megaprimer” method of PCR: increased template concentration improves yield. BioTechniques 10:489-490. - PubMed
-
- Blatter, F. R., G. Plunkett, III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. D. Collado-Vides, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davids, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

