Towards the identification of type II secretion signals in a nonacylated variant of pullulanase from Klebsiella oxytoca
- PMID: 16199575
- PMCID: PMC1251600
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.20.7045-7055.2005
Towards the identification of type II secretion signals in a nonacylated variant of pullulanase from Klebsiella oxytoca
Abstract
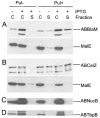
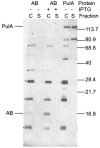
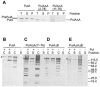
Pullulanase (PulA) from the gram-negative bacterium Klebsiella oxytoca is a 116-kDa surface-anchored lipoprotein of the isoamylase family that allows growth on branched maltodextrin polymers. PulA is specifically secreted via a type II secretion system. PelBsp-PulA, a nonacylated variant of PulA made by replacing the lipoprotein signal peptide (sp) with the signal peptide of pectate lyase PelB from Erwinia chrysanthemi, was efficiently secreted into the medium. Two 80-amino-acid regions of PulA, designated A and B, were previously shown to promote secretion of beta-lactamase (BlaM) and endoglucanase CelZ fused to the C terminus. We show that A and B fused to the PelB signal peptide can also promote secretion of BlaM and CelZ but not that of nuclease NucB or several other reporter proteins. However, the deletion of most of region A or all of region B, either individually or together, had only a minor effect on PelBsp-PulA secretion. Four independent linker insertions between amino acids 234 and 324 in PelBsp-PulA abolished secretion. This part of PulA, region C, could contain part of the PulA secretion signal or be important for its correct presentation. Deletion of region C abolished PelBsp-PulA secretion without dramatically affecting its stability. PelBsp-PulA-NucB chimeras were secreted only if the PulA-NucB fusion point was located downstream from region C. The data show that at least three regions of PulA contain information that influences its secretion, depending on their context, and that some reporter proteins might contribute to the secretion of chimeras of which they are a part.
Figures
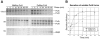



Similar articles
-
Extracellular secretion of pullulanase is unaffected by minor sequence changes but is usually prevented by adding reporter proteins to its N- or C-terminal end.J Bacteriol. 1995 Sep;177(18):5238-46. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.18.5238-5246.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7665512 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of two regions of Klebsiella oxytoca pullulanase that together are capable of promoting beta-lactamase secretion by the general secretory pathway.Mol Microbiol. 1996 Oct;22(1):1-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02650.x. Mol Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8899703
-
Stable periplasmic secretion intermediate in the general secretory pathway of Escherichia coli.EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):271-8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05653.x. EMBO J. 1993. PMID: 8428585 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Klebsiella pneumoniae genes for production, surface localization and secretion of the lipoprotein pullulanase.EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3531-8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02679.x. EMBO J. 1987. PMID: 3322811 Free PMC article.
-
Macromolecular assembly and secretion across the bacterial cell envelope: type II protein secretion systems.J Mol Biol. 1998 Jun 12;279(3):485-99. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1791. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9641973 Review.
Cited by
-
Many substrates and functions of type II secretion: lessons learned from Legionella pneumophila.Future Microbiol. 2009 Sep;4(7):797-805. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.53. Future Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19722835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of the lipoprotein N-acyltransferase in Bacteroides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2410909121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410909121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495918 Free PMC article.
-
Protein secretion and membrane insertion systems in gram-negative bacteria.J Membr Biol. 2006;214(2):75-90. doi: 10.1007/s00232-006-0049-7. Epub 2007 Jun 2. J Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 17546510 Review.
-
Type IV pilin proteins: versatile molecular modules.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Dec;76(4):740-72. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00035-12. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23204365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-function analysis of pectate lyase Pel3 reveals essential facets of protein recognition by the bacterial type 2 secretion system.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100305. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100305. Epub 2021 Jan 16. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33465378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouley, J., G. Condemine, and V. E. Shevchik. 2001. The PDZ domain of OutC and the N-terminal region of OutD determine the secretion specificity of the type II out pathway of Erwinia chrysanthemi. J. Mol. Biol. 27:205-219. - PubMed
-
- Brockman, R. W., and L. A. Heppel. 1968. On the localization of alkaline phosphatase and cyclic phosphodiesterase in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 7:2554-2562. - PubMed
-
- Broome-Smith, J. K., and B. G. Spratt. 1986. A vector for the construction of translational fusions to TEM beta-lactamase and the analysis of protein export signals and membrane protein topology. Gene 49:341-349. - PubMed
-
- Chapon, V., M. Czjzek, M. El Hassouni, B. Py, M. Juy, and F. Barras. 2001. Type II protein secretion in gram-negative pathogenic bacteria: the study of the structure/secretion relationships of the cellulase Cel5 (formerly EGZ) from Erwinia chrysanthemi. J. Mol. Biol. 310:1055-1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

