mTOR controls FLIPS translation and TRAIL sensitivity in glioblastoma multiforme cells
- PMID: 16199861
- PMCID: PMC1265779
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.8809-8823.2005
mTOR controls FLIPS translation and TRAIL sensitivity in glioblastoma multiforme cells
Abstract
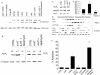
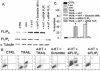
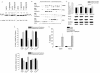
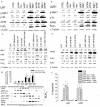
The tumor-selective, proapoptotic, death receptor ligand tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a mediator of antitumor drug activity and in itself is a promising agent for the treatment of human malignancies. Like many tumors, however, glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most fatal form of glioma, exhibits a range of TRAIL sensitivity, and only a small percentage of GBM tumors undergo TRAIL-induced apoptosis. We here show that TRAIL resistance in GBM is a consequence of overexpression of the short isoform of the caspase-8 inhibitor, c-FLICE inhibitory protein (FLIP(S)), and that FLIP(S) expression is in turn translationally enhanced by activation of the Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-p70 S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) pathway. Conversely, pharmacologic or genetic inhibition of mTOR, or the mTOR target S6K1, suppresses polyribosomal accumulation of FLIP(S) mRNA, FLIP(S) protein expression, and TRAIL resistance. In archived material from 12 human GBM tumors, PTEN status was a predictor of activation of the Akt-mTOR-S6K1 pathway and of FLIP(S) levels, while in xenografted human GBM, activation status of the PTEN-Akt-mTOR pathway distinguished the tumors inherently sensitive to TRAIL from those which could be sensitized by the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. These results define the mTOR pathway as a key limiter of tumor elimination by TRAIL-mediated mechanisms, provide a means by which the TRAIL-sensitive subset of GBM can be identified, and provide rationale for the combined use of TRAIL with mTOR inhibitors in the treatment of human cancers.
Figures









References
-
- Almasan, A., and A. Ashkenazi. 2003. Apo2L/TRAIL: apoptosis signaling, biology, and potential for cancer therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14:337-348. - PubMed
-
- Altucci, L., A. Rossin, W. Raffelsberger, A. Reitmair, C. Chomienee, and H. Gronemeyer. 2001. Retinoic acid-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells is mediated by paracrine action of tumor-selective death ligand TRAIL. Nat. Med. 7:680-686. - PubMed
-
- Bin, L., X. Li, L.-G. Xu, and H.-B. Shu. 2002. The short splice form of Casper/c-FLIP is a major cellular inhibitor of TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 510:37-40. - PubMed
-
- Blommaart, E. F., J. J. Luiken, P. J. Blommaart, G. M. van Woerkom, and A. J. Meijer. 1995. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 is inhibitory for autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 270:2320-2326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
