The amino-terminal region of Drosophila MSL1 contains basic, glycine-rich, and leucine zipper-like motifs that promote X chromosome binding, self-association, and MSL2 binding, respectively
- PMID: 16199870
- PMCID: PMC1265775
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.8913-8924.2005
The amino-terminal region of Drosophila MSL1 contains basic, glycine-rich, and leucine zipper-like motifs that promote X chromosome binding, self-association, and MSL2 binding, respectively
Abstract
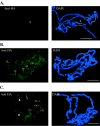
In Drosophila melanogaster, X chromosome dosage compensation is achieved by doubling the transcription of most X-linked genes. The male-specific lethal (MSL) complex is required for this process and binds to hundreds of sites on the male X chromosome. The MSL1 protein is essential for X chromosome binding and serves as a central scaffold for MSL complex assembly. We find that the amino-terminal region of MSL1 binds to hundreds of sites on the X chromosome in normal males but only to approximately 30 high-affinity sites in the absence of endogenous MSL1. Binding to the high-affinity sites requires a basic motif at the amino terminus that is conserved among Drosophila species. X chromosome binding also requires a conserved leucine zipper-like motif that binds to MSL2. A glycine-rich motif between the basic and leucine-zipper-like motifs mediates MSL1 self-association in vitro and binding of the amino-terminal region of MSL1 to the MSL complex assembled on the male X chromosome. We propose that the basic region may mediate DNA binding and that the glycine-rich region may promote the association of MSL complexes to closely adjacent sites on the X chromosome.
Figures






References
-
- Akhtar, A. 2003. Dosage compensation: an intertwined world of RNA and chromatin remodelling. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 13:161-169. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar, A., and P. B. Becker. 2000. Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 5:367-375. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar, A., D. Zink, and P. B. Becker. 2000. Chromodomains are protein-RNA interaction modules. Nature 407:405-409. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw, G. J., and B. S. Baker. 1995. The msl-2 dosage compensation gene of Drosophila encodes a putative DNA-binding protein whose expression is sex specifically regulated by Sex-lethal. Development 121:3245-3258. - PubMed
-
- Belote, J. M., and J. C. Lucchesi. 1980. Control of X chromosome transcription by the maleless gene in Drosophila. Nature 285:573-575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
