Phosphorylation of BLM, dissociation from topoisomerase IIIalpha, and colocalization with gamma-H2AX after topoisomerase I-induced replication damage
- PMID: 16199871
- PMCID: PMC1265790
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.20.8925-8937.2005
Phosphorylation of BLM, dissociation from topoisomerase IIIalpha, and colocalization with gamma-H2AX after topoisomerase I-induced replication damage
Abstract
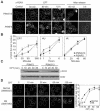
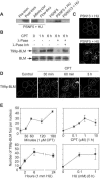
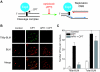
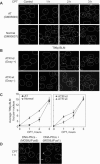
Topoisomerase I-associated DNA single-strand breaks selectively trapped by camptothecins are lethal after being converted to double-strand breaks by replication fork collisions. BLM (Bloom's syndrome protein), a RecQ DNA helicase, and topoisomerase IIIalpha (Top3alpha) appear essential for the resolution of stalled replication forks (Holliday junctions). We investigated the involvement of BLM in the signaling response to Top1-mediated replication DNA damage. In BLM-complemented cells, BLM colocalized with promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) nuclear bodies and Top3alpha. Fibroblasts without BLM showed an increased sensitivity to camptothecin, enhanced formation of Top1-DNA complexes, and delayed histone H2AX phosphorylation (gamma-H2AX). Camptothecin also induced nuclear relocalization of BLM, Top3alpha, and PML protein and replication-dependent phosphorylation of BLM on threonine 99 (T99p-BLM). T99p-BLM was also observed following replication stress induced by hydroxyurea. Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) protein and AT- and Rad9-related protein kinases, but not DNA-dependent protein kinase, appeared to play a redundant role in phosphorylating BLM. Following camptothecin treatment, T99p-BLM colocalized with gamma-H2AX but not with Top3alpha or PML. Thus, BLM appears to dissociate from Top3alpha and PML following its phosphorylation and facilitates H2AX phosphorylation in response to replication double-strand breaks induced by Top1. A defect in gamma-H2AX signaling in response to unrepaired replication-mediated double-strand breaks might, at least in part, explain the camptothecin-sensitivity of BLM-deficient cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Endogenous gamma-H2AX-ATM-Chk2 checkpoint activation in Bloom's syndrome helicase deficient cells is related to DNA replication arrested forks.Mol Cancer Res. 2007 Jul;5(7):713-24. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0028. Mol Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17634426
-
Regulation and localization of the Bloom syndrome protein in response to DNA damage.J Cell Biol. 2001 Apr 16;153(2):367-80. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.2.367. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11309417 Free PMC article.
-
ATR and ATM-dependent movement of BLM helicase during replication stress ensures optimal ATM activation and 53BP1 focus formation.Cell Cycle. 2004 Dec;3(12):1579-86. doi: 10.4161/cc.3.12.1286. Epub 2004 Dec 4. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15539948
-
Functions of RecQ family helicases: possible involvement of Bloom's and Werner's syndrome gene products in guarding genome integrity during DNA replication.J Biochem. 2001 Apr;129(4):501-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002883. J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11275547 Review.
-
Role of the BLM helicase in replication fork management.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Jul 1;6(7):936-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Mar 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17363339 Review.
Cited by
-
The G-quadruplex ligand telomestatin impairs binding of topoisomerase IIIalpha to G-quadruplex-forming oligonucleotides and uncaps telomeres in ALT cells.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 9;4(9):e6919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006919. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19742304 Free PMC article.
-
A helical bundle in the N-terminal domain of the BLM helicase mediates dimer and potentially hexamer formation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 7;292(14):5909-5920. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.761510. Epub 2017 Feb 22. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28228481 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-causing missense mutations in human DNA helicase disorders.Mutat Res. 2013 Apr-Jun;752(2):138-152. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2012.12.004. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23276657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Prevalence and Roles of Proteins Undergoing Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in the Biogenesis of PML-Bodies.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 18;13(12):1805. doi: 10.3390/biom13121805. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136675 Free PMC article.
-
Rising from the RecQ-age: the role of human RecQ helicases in genome maintenance.Trends Biochem Sci. 2008 Dec;33(12):609-20. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.09.003. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008. PMID: 18926708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ababou, M., V. Dumaire, Y. Lecluse, and M. Amor-Gueret. 2002. Bloom's syndrome protein response to ultraviolet-C radiation and hydroxyurea-mediated DNA synthesis inhibition. Oncogene 21:2079-2088. - PubMed
-
- Ababou, M., S. Dutertre, Y. Lecluse, R. Onclercq, B. Chatton, and M. Amor-Gueret. 2000. ATM-dependent phosphorylation and accumulation of endogenous BLM protein in response to ionizing radiation. Oncogene 19:5955-5963. - PubMed
-
- Aladjem, M. I., S. Pasa, S. Parodi, J. N. Weinstein, Y. Pommier, and K. W. Kohn. 2004. Molecular interaction maps—a diagrammatic graphical language for bioregulatory networks. Sci. STKE 2004:pe8. - PubMed
-
- Barnett, A. A. 1996. FDA approve bark-derived drug. Lancet 347:1613. - PubMed
-
- Bassing, C. H., and F. W. Alt. 2004. H2AX may function as an anchor to hold broken chromosomal DNA ends in close proximity. Cell Cycle 3:149-153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
