The survival kinases Akt and Pim as potential pharmacological targets
- PMID: 16200194
- PMCID: PMC1236693
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26273
The survival kinases Akt and Pim as potential pharmacological targets
Abstract
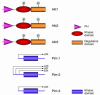
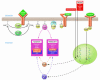
The Akt and Pim kinases are cytoplasmic serine/threonine kinases that control programmed cell death by phosphorylating substrates that regulate both apoptosis and cellular metabolism. The PI3K-dependent activation of the Akt kinases and the JAK/STAT-dependent induction of the Pim kinases are examples of partially overlapping survival kinase pathways. Pharmacological manipulation of such kinases could have a major impact on the treatment of a wide variety of human diseases including cancer, inflammatory disorders, and ischemic diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Kawauchi K, Ogasawara T, Yasuyama M, Ohkawa S. Involvement of Akt kinase in the action of STI571 on chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2003;31:11–17. - PubMed
-
- Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J. Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 2004;305:1163–1167. - PubMed
-
- Wendel HG, et al. Survival signalling by Akt and eIF4E in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature. 2004;428:332–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

