Death versus survival: functional interaction between the apoptotic and stress-inducible heat shock protein pathways
- PMID: 16200196
- PMCID: PMC1236700
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26471
Death versus survival: functional interaction between the apoptotic and stress-inducible heat shock protein pathways
Abstract
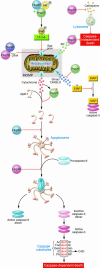
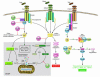
Induction of heat shock proteins (Hsps) following cellular damage can prevent apoptosis induced by both the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic pathway is characterized by mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), cytochrome c release, apoptosome assembly, and caspase activation. Hsps promote cell survival by preventing MOMP or apoptosome formation as well as via regulation of Akt and JNK activities. Engagement of the TNF death receptors induces the extrinsic pathway that is characterized by Fas-associated death domain-dependent (FADD-dependent) caspase-8 activation or induction of NF-kappaB to promote cellular survival. Hsps can directly suppress proapoptotic signaling events or stabilizing elements of the NF-kappaB pathway to promote cellular survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"The stress of dying": the role of heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis.J Cell Sci. 2004 Jun 1;117(Pt 13):2641-51. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01284. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15169835 Review.
-
NF-kappaB stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthase to protect mouse hepatocytes from TNF-alpha- and Fas-mediated apoptosis.Gastroenterology. 2001 Apr;120(5):1251-62. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.23239. Gastroenterology. 2001. PMID: 11266388
-
Indomethacin induces apoptosis in 786-O renal cell carcinoma cells by activating mitogen-activated protein kinases and AKT.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jun 1;563(1-3):49-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.071. Epub 2007 Feb 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17341418
-
Fas (CD95) ligation inhibits activation of NF-kappa B by targeting p65-Rel A in a caspase-dependent manner.Clin Immunol. 2006 Oct;121(1):47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.04.572. Epub 2006 Jun 9. Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16765090
-
Heat shock genes - integrating cell survival and death.J Biosci. 2007 Apr;32(3):595-610. doi: 10.1007/s12038-007-0059-3. J Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17536179 Review.
Cited by
-
HSP90 Inhibition and Modulation of the Proteome: Therapeutical Implications for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 25;21(15):5286. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155286. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32722485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Muscle Tissue Development in Beef Cattle.Genes (Basel). 2020 Mar 11;11(3):295. doi: 10.3390/genes11030295. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32168744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSP70 interacts with TRAF2 and differentially regulates TNFalpha signalling in human colon cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Mar;14(3):710-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00716.x. Epub 2009 Feb 20. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 19243468 Free PMC article.
-
Transcript analysis of heat shock protein 72 in vitrified 2-cell mouse embryos and subsequent in vitro development.Cell J. 2014 Winter;15(4):340-7. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Cell J. 2014. PMID: 24381859 Free PMC article.
-
A kinase-independent role for unoccupied insulin and IGF-1 receptors in the control of apoptosis.Sci Signal. 2010 Dec 7;3(151):ra87. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001173. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 21139139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beere, H.M. 2001. Stressed to death: regulation of apoptotic signaling pathways by the heat shock proteins. Sci. STKE. doi:10.1126/stke.2001.93.re1. - PubMed
-
- Beere HM, Green DR. Stress management: heat shock protein-70 and the regulation of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Beere HM. “The stress of dying”: the role of heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis. J. Cell Sci. 2004;117:2641–2651. - PubMed
-
- Parsell DA, Lindquist S. The function of heat-shock proteins in stress tolerance: degradation and reactivation of damaged proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1993;27:437–496. - PubMed
-
- Nollen EAA, Morimoto RI. Chaperoning signaling pathways: molecular chaperones as stress-sensing ‘heat shock’ proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:2809–2816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

