PDGF signaling in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 16200204
- PMCID: PMC1236701
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26593
PDGF signaling in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
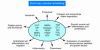
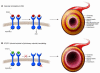
The pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) includes endothelial cell dysfunction and proliferation and migration of VSMCs. As PDGF has been implicated in these processes, Schermuly et al. hypothesized that altered PDGF signaling may be involved in the vascular remodeling observed in PAH. To explore this notion further, the authors evaluated the effects of the PDGF receptor inhibitor STI571 in 2 different animal models of pulmonary hypertension. In both models, after development of pulmonary vascular disease, administration of STI571 reversed pulmonary vascular changes. These studies provide preclinical proof of concept for the clinical development of a PDGF inhibitor as a targeted therapy for PAH patients.
Figures
Comment on
-
Reversal of experimental pulmonary hypertension by PDGF inhibition.J Clin Invest. 2005 Oct;115(10):2811-21. doi: 10.1172/JCI24838. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16200212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Humbert M, Sitbon O, Simonneau G. Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;351:1425–1436. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, et al. A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy in primary pulmonary hypertension. The Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;334:296–301. - PubMed
-
- Rubin LJ, et al. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:896–903. - PubMed
-
- Galie, N., et al. 2005. Sildenafil citrate therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. In press. - PubMed
-
- Stenmark KR, Gerasimovskaya E, Nemenoff RA, Das M. Hypoxic activation of adventitial fibroblasts: role in vascular remodeling. Chest. 2002;122:326S–334S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

