Reversal of experimental pulmonary hypertension by PDGF inhibition
- PMID: 16200212
- PMCID: PMC1236676
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI24838
Reversal of experimental pulmonary hypertension by PDGF inhibition
Abstract
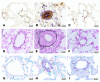
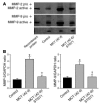
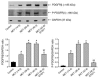
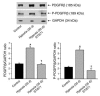
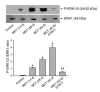
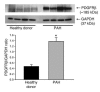
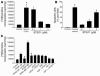
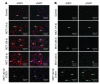
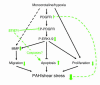
Progression of pulmonary hypertension is associated with increased proliferation and migration of pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells. PDGF is a potent mitogen and involved in this process. We now report that the PDGF receptor antagonist STI571 (imatinib) reversed advanced pulmonary vascular disease in 2 animal models of pulmonary hypertension. In rats with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension, therapy with daily administration of STI571 was started 28 days after induction of the disease. A 2-week treatment resulted in 100% survival, compared with only 50% in sham-treated rats. The changes in RV pressure, measured continuously by telemetry, and right heart hypertrophy were reversed to near-normal levels. STI571 prevented phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor and suppressed activation of downstream signaling pathways. Similar results were obtained in chronically hypoxic mice, which were treated with STI571 after full establishment of pulmonary hypertension. Moreover, expression of the PDGF receptor was found to be significantly increased in lung tissue from pulmonary arterial hypertension patients compared with healthy donor lung tissue. We conclude that STI571 reverses vascular remodeling and cor pulmonale in severe experimental pulmonary hypertension regardless of the initiating stimulus. This regimen offers a unique novel approach for antire-modeling therapy in progressed pulmonary hypertension.
Figures
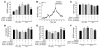
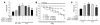
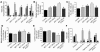
Comment in
-
PDGF signaling in pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Clin Invest. 2005 Oct;115(10):2691-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI26593. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16200204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Humbert M, Sitbon O, Simonneau G. Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;351:1425–1436. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, et al. A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. The Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;334:296–302. - PubMed
-
- Olschewski H, et al. Inhaled iloprost for severe pulmonary hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;347:322–329. - PubMed
-
- Rubin LJ, et al. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:896–903. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, et al. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004;43:13S–24S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

