Nkx3.1 binds and negatively regulates the transcriptional activity of Sp-family members in prostate-derived cells
- PMID: 16201967
- PMCID: PMC1383699
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051030
Nkx3.1 binds and negatively regulates the transcriptional activity of Sp-family members in prostate-derived cells
Abstract
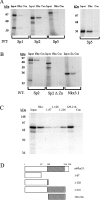
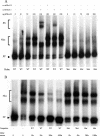
Nkx3.1 is a homeodomain-containing transcription factor that is expressed early in the development of the prostate gland and is believed to play an important role in the differentiation of prostatic epithelia. Loss of Nkx3.1 protein expression is often an early event in prostate tumorigenesis, and the abundance of Nkx3.1-negative epithelial cells increases with disease progression. In a number of systems, homeodomain proteins collaborate with zinc-finger-containing transcription factors to bind and regulate target genes. In the present paper, we report that Nkx3.1 collaborates with Sp-family members in the regulation of PSA (prostate-specific antigen) in prostate-derived cells. Nkx3.1 forms protein complexes with Sp proteins that are dependent on their respective DNA-binding domains and an N-terminal segment of Nkx3.1, and Nkx3.1 negatively regulates Sp-mediated transcription via Trichostatin A-sensitive and -insensitive mechanisms. A distal 1000 bp portion of the PSA promoter is required for transrepression by Nkx3.1, although Nkx3.1 DNA-binding activity is itself not required. We conclude that Nkx3.1 negatively regulates Sp-mediated transcription via the tethering of histone deacetylases and/or by inhibiting the association of Sp proteins with co-activators.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Structural and functional analysis of domains mediating interaction between the bagpipe homologue, Nkx3.1 and serum response factor.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008 Mar;233(3):297-309. doi: 10.3181/0709-RM-236. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008. PMID: 18296735
-
p53 overexpression represses androgen-mediated induction of NKX3.1 in a prostate cancer cell line.Exp Mol Med. 2006 Dec 31;38(6):625-33. doi: 10.1038/emm.2006.74. Exp Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 17202838
-
Mechanisms of prostate tumorigenesis: roles for transcription factors Nkx3.1 and Egr1.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Nov;1059:33-40. doi: 10.1196/annals.1339.018. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16382041 Review.
-
Physical and functional interactions between the prostate suppressor homeoprotein NKX3.1 and serum response factor.J Mol Biol. 2006 Jul 28;360(5):989-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.064. Epub 2006 Jun 15. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16814806
-
Regulating NKX3.1 stability and function: Post-translational modifications and structural determinants.Prostate. 2016 May;76(6):523-33. doi: 10.1002/pros.23144. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Prostate. 2016. PMID: 26841725 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of MEOX1 and MEOX2 regulation of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p16 in vascular endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029099. Epub 2011 Dec 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22206000 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of two functional NKX3.1 binding sites upstream of the PCAN1 gene that are involved in the positive regulation of PCAN1 gene transcription.BMC Mol Biol. 2008 May 4;9:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-45. BMC Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18454873 Free PMC article.
-
TWIST1, A novel androgen-regulated gene, is a target for NKX3-1 in prostate cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 Jan 31;13(1):4. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-4. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23368843 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring TF activation order in time series scRNA-Seq studies.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Feb 18;16(2):e1007644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007644. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32069291 Free PMC article.
-
Sp2 is a maternally inherited transcription factor required for embryonic development.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 5;285(6):4153-4164. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.078881. Epub 2009 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19959469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sciavolino P. J., Abrams E. W., Yang L., Austenberg L. P., Shen M. M., Abate-Shen C. Tissue-specific expression of murine Nkx3.1 in the male urogenital system. Dev. Dyn. 1997;209:127–138. - PubMed
-
- He W. W., Sciavolino P. J., Wing J., Augustus M., Hudson P., Meissner P. S., Curtis R. T., Shell B. K., Bostwick D. G., Tindall D. J., et al. A novel human prostate-specific, androgen-regulated homeobox gene (Nkx3.1) that maps to 8p21, a region frequently deleted in prostate cancer. Genomics. 1997;43:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Bowen C., Bubendorf L., Voeller H. J., Slack R., Willi N., Sauter G., Gasser T. C., Konisto P., Lack E. E., Kononen J., et al. Loss of Nkx3.1 expression in human prostate cancers correlates with tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6111–6115. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka M., Komuro I., Inagaki H., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Izumo S. Nkx3.1, a murine homolog of Drosophila bagpipe, regulates epithelial ductal branching and proliferation of the prostate and palatine glands. Dev. Dyn. 2000;219:248–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

