Integrin-linked kinase is responsible for Ca2+-independent myosin diphosphorylation and contraction of vascular smooth muscle
- PMID: 16201970
- PMCID: PMC1316305
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051173
Integrin-linked kinase is responsible for Ca2+-independent myosin diphosphorylation and contraction of vascular smooth muscle
Abstract
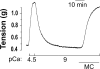
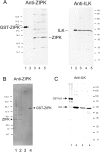
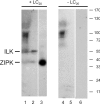
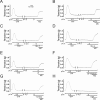
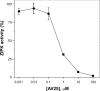
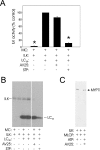
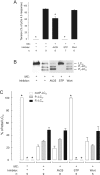
Smooth muscle contraction is activated by phosphorylation at Ser-19 of LC20 (the 20 kDa light chains of myosin II) by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent MLCK (myosin light-chain kinase). Diphosphorylation of LC20 at Ser-19 and Thr-18 is observed in smooth muscle tissues and cultured cells in response to various contractile stimuli, and in pathological circumstances associated with hypercontractility. MLCP (myosin light-chain phosphatase) inhibition can lead to LC20 diphosphorylation and Ca2+-independent contraction, which is not attributable to MLCK. Two kinases have emerged as candidates for Ca2+-independent LC20 diphosphorylation: ILK (integrin-linked kinase) and ZIPK (zipper-interacting protein kinase). Triton X-100-skinned rat caudal arterial smooth muscle was used to investigate the relative importance of ILK and ZIPK in Ca2+-independent, microcystin (phosphatase inhibitor)-induced LC20 diphosphorylation and contraction. Western blotting and in-gel kinase assays revealed that both kinases were retained in this preparation. Ca2+-independent contraction of calmodulin-depleted tissue in response to microcystin was resistant to MLCK inhibitors [AV25 (a 25-amino-acid peptide derived from the autoinhibitory domain of MLCK), ML-7, ML-9 and wortmannin], protein kinase C inhibitor (GF109203X) and Rho-associated kinase inhibitors (Y-27632 and H-1152), but blocked by the non-selective kinase inhibitor staurosporine. ZIPK was inhibited by AV25 (IC50 0.63+/-0.05 microM), whereas ILK was insensitive to AV25 (at concentrations as high as 100 microM). AV25 had no effect on Ca2+-independent, microcystin-induced LC20 mono- or di-phosphorylation, with a modest effect on force. We conclude that direct inhibition of MLCP in the absence of Ca2+ unmasks ILK activity, which phosphorylates LC20 at Ser-19 and Thr-18 to induce contraction. ILK is probably the kinase responsible for myosin diphosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells and tissues.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ca2+-independent phosphorylation of myosin in rat caudal artery and chicken gizzard myofilaments.J Physiol. 1999 May 1;516 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):805-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0805u.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10200427 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+-independent contraction of longitudinal ileal smooth muscle is potentiated by a zipper-interacting protein kinase pseudosubstrate peptide.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):G361-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00112.2009. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19541925
-
Characterization of protein kinase pathways responsible for Ca2+ sensitization in rat ileal longitudinal smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):G699-710. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00214.2007. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17656444
-
The regulation of smooth muscle contractility by zipper-interacting protein kinase.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Jan;85(1):79-87. doi: 10.1139/y06-103. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17487247 Review.
-
Involvement of myosin regulatory light chain diphosphorylation in sustained vasoconstriction under pathophysiological conditions.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2014;50:18-28. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.50.18. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2014. PMID: 24770446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitor κB kinase 2 is a myosin light chain kinase in vascular smooth muscle.Circ Res. 2013 Aug 16;113(5):562-70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301510. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23817200 Free PMC article.
-
PDMS Elastic Micropost Arrays for Studying Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2013 Nov 1;188:1055-1063. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2013.08.018. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2013. PMID: 26451074 Free PMC article.
-
Cdk5-dependent regulation of Rho activity, cytoskeletal contraction, and epithelial cell migration via suppression of Src and p190RhoGAP.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(24):6488-99. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01098-09. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19822667 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through myosin light chain kinase in smooth muscles.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 15;288(11):7596-7605. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.427112. Epub 2013 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23362260 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-parvin controls vascular mural cell recruitment to vessel wall by regulating RhoA/ROCK signalling.EMBO J. 2009 Oct 21;28(20):3132-44. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.295. Epub 2009 Oct 1. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19798050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Dedicated myosin light chain kinases with diverse cellular functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:4527–4530. - PubMed
-
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin II: modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol. Rev. 2003;83:1325–1358. - PubMed
-
- Hartshorne D. J., Ito M., Erdödi F. Role of protein phosphatase type 1 in contractile functions: myosin phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:37211–37214. - PubMed
-
- Ito M., Nakano T., Erdödi F., Hartshorne D. J. Myosin phosphatase: structure, regulation and function. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004;259:197–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

