Adenosine and deoxyadenosine induces apoptosis in oestrogen receptor-positive and -negative human breast cancer cells via the intrinsic pathway
- PMID: 16202036
- PMCID: PMC6495740
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2005.00349.x
Adenosine and deoxyadenosine induces apoptosis in oestrogen receptor-positive and -negative human breast cancer cells via the intrinsic pathway
Abstract
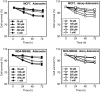
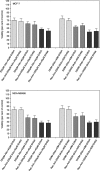
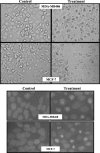
In this study we have examined the cytotoxic effects of different concentrations of adenosine (Ado) and deoxyadenosine (dAdo) on human breast cancer cell lines. Ado and dAdo alone had little effect on cell cytotoxicity. However, in the presence of adenosine deaminase (ADA) inhibitor, EHNA, adenosine and deoxyadenosine led to significant growth inhibition of cells of the lines tested. Ado/EHNA and dAdo/EHNA-induced cell death was significantly inhibited by NBTI, an inhibitor of nucleoside transport, and 5'-amino-5'-deoxyadenosine, an inhibitor of adenosine kinase, but the effects were not affected by 8-phenyltheophylline, a broad inhibitor of adenosine receptors. The Ado/EHNA combination brought about morphological changes consistent with apoptosis. Caspase-9 activation was observed in MCF-7 and MDA-MB468 human breast cancer cell lines on treatment with Ado/EHNA or dAdo/EHNA, but, as expected, caspase-3 activation was only observed in MDA-MB468 cells. The results of the study, thus, suggest that extracellular adenosine and deoxyadenosine induce apoptosis in both oestrogen receptor-positive (MCF-7) and also oestrogen receptor-negative (MDA-MB468) human breast cancer cells by its uptake into the cells and conversion to AMP (dAMP) followed by activation of nucleoside kinase, and finally by the activation of the mitochondrial/intrinsic apoptotic pathway.
Figures






References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Ceruti S, Brambilla R, Franceschi C, Malorni W, Jacobson KA, von Lubitz DK, Cattabeni F (1997) Modulation of apoptosis by adenosine in the central nervous system: a possible role for the A3 receptor. Pathophysiological significance and therapeutic implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 825, 11. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barczyk K, Kreuter M, Pryjma J, Booy EP, Maddika S, Ghavami S, Berdel WE, Roth J, Los M (2005) Serum cytochrome c indicates in vivo apoptosis and it can serve as a prognostic marker during cancer therapy. Int. J. Cancer 114, 167. - PubMed
-
- Barry CP, Lind SE (2000) Adenosine‐mediated killing of cultured epithelial cancer cells. Cancer Res. 60, 1887. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantities of microgram of protein utilizing the principle of protein‐dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

