Combining RNA interference and kinase inhibitors against cell signalling components involved in cancer
- PMID: 16202132
- PMCID: PMC1262698
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-125
Combining RNA interference and kinase inhibitors against cell signalling components involved in cancer
Abstract
Background: The transcription factor activator protein-1 (AP-1) has been implicated in a large variety of biological processes including oncogenic transformation. The tyrosine kinases of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) constitute the beginning of one signal transduction cascade leading to AP-1 activation and are known to control cell proliferation and differentiation. Drug discovery efforts targeting this receptor and other pathway components have centred on monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors. Resistance to such inhibitors has already been observed, guiding the prediction of their use in combination therapies with other targeted agents such as RNA interference (RNAi). This study examines the use of RNAi and kinase inhibitors for qualification of components involved in the EGFR/AP-1 pathway of ME180 cells, and their inhibitory effects when evaluated individually or in tandem against multiple components of this important disease-related pathway.
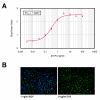
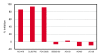
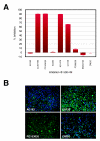
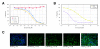
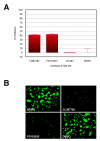
Methods: AP-1 activation was assessed using an ME180 cell line stably transfected with a beta-lactamase reporter gene under the control of AP-1 response element following epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation. Immunocytochemistry allowed for further quantification of small molecule inhibition on a cellular protein level. RNAi and RT-qPCR experiments were performed to assess the amount of knockdown on an mRNA level, and immunocytochemistry was used to reveal cellular protein levels for the targeted pathway components.
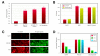
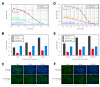
Results: Increased potency of kinase inhibitors was shown by combining RNAi directed towards EGFR and small molecule inhibitors acting at proximal or distal points in the pathway. After cellular stimulation with EGF and analysis at the level of AP-1 activation using a beta-lactamase reporter gene, a 10-12 fold shift or 2.5-3 fold shift toward greater potency in the IC50 was observed for EGFR and MEK-1 inhibitors, respectively, in the presence of RNAi targeting EGFR.
Conclusion: EGFR pathway components were qualified as targets for inhibition of AP-1 activation using RNAi and small molecule inhibitors. The combination of these two targeted agents was shown to increase the efficacy of EGFR and MEK-1 kinase inhibitors, leading to possible implications for overcoming or preventing drug resistance, lowering effective drug doses, and providing new strategies for interrogating cellular signalling pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II regulation of TGF-beta in murine mesangial cells involves both PI3 kinase and MAP kinase.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2004 Summer;34(3):277-86. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2004. PMID: 15487702
-
Increase in claudin-2 expression by an EGFR/MEK/ERK/c-Fos pathway in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1823(6):1110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.04.005. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22546605
-
Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cells: the effect of combining RNA interference with tyrosine kinase inhibitors or cetuximab.BMC Med. 2012 Mar 21;10:28. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-28. BMC Med. 2012. PMID: 22436374 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Jun;15(2):420-34. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8229-y. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23575987 Review.
-
Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012 Jan;16(1):15-31. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.648617. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012. PMID: 22239438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing of Parkinson's disease-associated genes with artificial mirtron mimics of miR-1224.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(19):9863-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks712. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22848108 Free PMC article.
-
MEK5/ERK5 pathway: the first fifteen years.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1825(1):37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22020294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms that Regulate Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inactivation.Clin Med Oncol. 2008;2:47-61. doi: 10.4137/cmo.s498. Epub 2008 Feb 9. Clin Med Oncol. 2008. PMID: 21892266 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling of the dose response: a more powerful approach for characterizing drug activities.PLoS Comput Biol. 2009 Sep;5(9):e1000512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000512. Epub 2009 Sep 18. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009. PMID: 19763178 Free PMC article.
-
Novel RNA-based strategies for therapeutic gene silencing.Mol Ther. 2010 Mar;18(3):466-76. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.306. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Mol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20087319 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

