Ultrafine particles cause cytoskeletal dysfunctions in macrophages: role of intracellular calcium
- PMID: 16202162
- PMCID: PMC1262770
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-8977-2-7
Ultrafine particles cause cytoskeletal dysfunctions in macrophages: role of intracellular calcium
Abstract
Background: Particulate air pollution is reported to cause adverse health effects in susceptible individuals. Since most of these particles are derived form combustion processes, the primary composition product is carbon with a very small diameter (ultrafine, less than 100 nm in diameter). Besides the induction of reactive oxygen species and inflammation, ultrafine particles (UFP) can cause intracellular calcium transients and suppression of defense mechanisms of alveolar macrophages, such as impaired migration or phagocytosis.
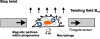
Methods: In this study the role of intracellular calcium transients caused by UFP was studied on cytoskeleton related functions in J774A.1 macrophages. Different types of fine and ultrafine carbon black particles (CB and ufCB, respectively), such as elemental carbon (EC90), commercial carbon (Printex 90), diesel particulate matter (DEP) and urban dust (UD), were investigated. Phagosome transport mechanisms and mechanical cytoskeletal integrity were studied by cytomagnetometry and cell viability was studied by fluorescence microscopy. Macrophages were exposed in vitro with 100 and 320 microg UFP/ml/million cells for 4 hours in serum free medium. Calcium antagonists Verapamil, BAPTA-AM and W-7 were used to block calcium channels in the membrane, to chelate intracellular calcium or to inhibit the calmodulin signaling pathways, respectively.
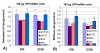
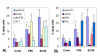
Results: Impaired phagosome transport and increased cytoskeletal stiffness occurred at EC90 and P90 concentrations of 100 microg/ml/million cells and above, but not with DEP or UD. Verapamil and W-7, but not BAPTA-AM inhibited the cytoskeletal dysfunctions caused by EC90 or P90. Additionally the presence of 5% serum or 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) suppressed the cytoskeletal dysfunctions. Cell viability showed similar results, where co-culture of ufCB together with Verapamil, W-7, FCS or BSA produced less cell dead compared to the particles only.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ultrafine particles cause cytoskeletal dysfunctions in macrophages.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Aug 1;182(3):197-207. doi: 10.1006/taap.2002.9430. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12183099
-
Calcium and ROS-mediated activation of transcription factors and TNF-alpha cytokine gene expression in macrophages exposed to ultrafine particles.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004 Feb;286(2):L344-53. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00139.2003. Epub 2003 Oct 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14555462
-
Increased inflammation and intracellular calcium caused by ultrafine carbon black is independent of transition metals or other soluble components.Occup Environ Med. 2000 Oct;57(10):685-91. doi: 10.1136/oem.57.10.685. Occup Environ Med. 2000. PMID: 10984341 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cytokine production in human alveolar macrophages and airway epithelial cells in response to ambient air pollution particles: further mechanistic studies.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005 Sep 1;207(2 Suppl):269-75. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.01.023. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15993911 Review.
-
Significance of particle parameters in the evaluation of exposure-dose-response relationships of inhaled particles.Inhal Toxicol. 1996;8 Suppl:73-89. Inhal Toxicol. 1996. PMID: 11542496 Review.
Cited by
-
PM2.5 Synergizes With Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Suppress Alveolar Macrophage Function in Mice Through the mTOR Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 21;13:924242. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.924242. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35800443 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrafine Particulate Matter Increases Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2017 Oct;17(4):441-450. doi: 10.1007/s12012-017-9402-6. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28194639 Free PMC article.
-
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from smokers release higher levels of IL-1-like cytokines after exposure to combustion-generated ultrafine particles.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 22;7:43016. doi: 10.1038/srep43016. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28223692 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of PM10 in human peripheral blood monocytes and J774 macrophages.Respir Res. 2004 Dec 21;5(1):29. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-5-29. Respir Res. 2004. PMID: 15613243 Free PMC article.
-
Biopharmaceutics and therapeutic potential of engineered nanomaterials.Curr Drug Metab. 2008 Oct;9(8):697-709. doi: 10.2174/138920008786049230. Curr Drug Metab. 2008. PMID: 18855608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pope CA, Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM, Dockery DW, Evans JS, Speizer FE, Heath CW. Particulate air pollution as a predictor of mortality in a prospective study of U.S. adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:669–674. - PubMed
-
- Peters A, Wichmann HE, Tuch T, Heinrich J, Heyder J. Respiratory effects are associated with the number of ultrafine particles. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;155:1376–1383. - PubMed
-
- Wichmann HE, Spix C, Tuch T, Wölke G, Peters A, Heinrich J, Kreyling WG, Heyder J. Daily mortality and fine and ultrafine particles in Erfurt, Germany part I: role of particle number and particle mass. Research report/HEI. 2000;98:5–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

