Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: an update
- PMID: 16202170
- PMCID: PMC1262784
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-9560-3-14
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: an update
Abstract
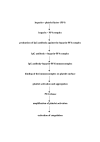
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is the most important and most frequent drug-induced, immune-mediated type of thrombocytopenia. It is associated with significant morbidity and mortality if unrecognized. In this review, we briefly discuss the main features of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, particularly analyzing the most recent advances in the pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of this syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Cines DB, Bussel JB, McMillan RB, Zehnder JL. Congenital and acquired thrombocytopenia. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) 2004:390–406. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources