The CATERPILLER protein monarch-1 is an antagonist of toll-like receptor-, tumor necrosis factor alpha-, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced pro-inflammatory signals
- PMID: 16203735
- PMCID: PMC4422647
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M502820200
The CATERPILLER protein monarch-1 is an antagonist of toll-like receptor-, tumor necrosis factor alpha-, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced pro-inflammatory signals
Abstract
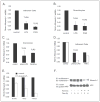
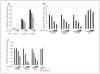
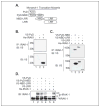
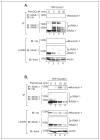
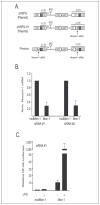
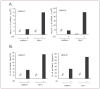
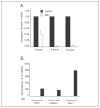
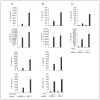
The CATERPILLER (CLR, also NOD and NLR) proteins share structural similarities with the nucleotide binding domain (NBD)-leucine-rich repeat (LRR) superfamily of plant disease-resistance (R) proteins and are emerging as important immune regulators in animals. CLR proteins contain NBD-LRR motifs and are linked to a limited number of distinct N-terminal domains including transactivation, CARD (caspase activation and recruitment), and pyrin domains (PyD). The CLR gene, Monarch-1/Pypaf7, is expressed by resting primary myeloid/monocytic cells, and its expression in these cells is reduced by Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Monarch-1 reduces NFkappaB activation by TLR-signaling molecules MyD88, IRAK-1 (type I interleukin-1 receptor-associated protein kinase), and TRAF6 (TNF receptor (TNFR)-associated factor) as well as TNFR signaling molecules TRAF2 and RIP1 but not the downstream NFkappaB subunit p65. This indicates that Monarch-1 is a negative regulator of both TLR and TNFR pathways. Reducing Monarch-1 expression with small interference RNA in myeloid/monocytic cells caused a dramatic increase in NFkappaB activation and cytokine expression in response to TLR2/TLR4 agonists, TNFalpha, or M. tuberculosis infection, suggesting that Monarch-1 is a negative regulator of inflammation. Because Monarch-1 is the first CLR protein that interferes with both TLR2 and TLR4 activation, the mechanism of this interference is significant. We find that Monarch-1 associates with IRAK-1 but not MyD88, resulting in the blockage of IRAK-1 hyperphosphorylation. Mutants containing the NBD-LRR or PyD-NBD also blocked IRAK-1 activation. This is the first example of a CLR protein that antagonizes inflammatory responses initiated by TLR agonists via interference with IRAK-1 activation.
Figures

References
-
- Harton JA, Linhoff MW, Zhang J, Ting JP. J Immunol. 2002;169:4088–4093. - PubMed
-
- Inohara N, Nunez G. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:371–382. - PubMed
-
- Tschopp J, Martinon F, Burns K. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:95–104. - PubMed
-
- Pawlowski K, Pio F, Chu Z, Reed JC, Godzik A. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:85–87. - PubMed
-
- Martinon F, Hofmann K, Tschopp J. Curr Biol. 2001;11:118–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

