Macroautophagy--a novel Beta-amyloid peptide-generating pathway activated in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 16203860
- PMCID: PMC2171227
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200505082
Macroautophagy--a novel Beta-amyloid peptide-generating pathway activated in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
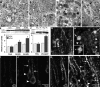
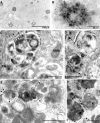
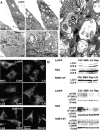
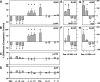
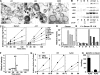
Macroautophagy, which is a lysosomal pathway for the turnover of organelles and long-lived proteins, is a key determinant of cell survival and longevity. In this study, we show that neuronal macroautophagy is induced early in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and before beta-amyloid (Abeta) deposits extracellularly in the presenilin (PS) 1/Abeta precursor protein (APP) mouse model of beta-amyloidosis. Subsequently, autophagosomes and late autophagic vacuoles (AVs) accumulate markedly in dystrophic dendrites, implying an impaired maturation of AVs to lysosomes. Immunolabeling identifies AVs in the brain as a major reservoir of intracellular Abeta. Purified AVs contain APP and beta-cleaved APP and are highly enriched in PS1, nicastrin, and PS-dependent gamma-secretase activity. Inducing or inhibiting macroautophagy in neuronal and nonneuronal cells by modulating mammalian target of rapamycin kinase elicits parallel changes in AV proliferation and Abeta production. Our results, therefore, link beta-amyloidogenic and cell survival pathways through macroautophagy, which is activated and is abnormal in AD.
Figures


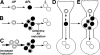
Comment in
-
A(beta) generation in autophagic vacuoles.J Cell Biol. 2005 Oct 10;171(1):15-7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200508097. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16216920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asanuma, K., I. Tanida, I. Shirato, T. Ueno, H. Takahara, T. Nishitani, E. Kominami, and Y. Tomino. 2003. MAP-LC3, a promising autophagosomal marker, is processed during the differentiation and recovery of podocytes from PAN nephrosis. FASEB J. 17:1165–1167. - PubMed
-
- Askanas, V., W.K. Engel, C.C. Yang, R.B. Alvarez, V.M. Lee, and T. Wisniewski. 1998. Light and electron microscopic immunolocalization of presenilin 1 in abnormal muscle fibers of patients with sporadic inclusion-body myositis and autosomal-recessive inclusion-body myopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 152:889–895. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bendiske, J., and B.A. Bahr. 2003. Lysosomal activation is a compensatory response against protein accumulation and associated synaptopathogenesis-an approach for slowing Alzheimer disease? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62:451–463. - PubMed
-
- Biederbick, A., H.F. Kern, and H.P. Elsasser. 1995. Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for autophagic vacuoles. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 66:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Billings, L.M., S. Oddo, K.N. Green, J.L. McGaugh, and F.M. Laferla. 2005. Intraneuronal Aβ causes the onset of early Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron. 45:675–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

