Cyclophilin A is required for TRIM5{alpha}-mediated resistance to HIV-1 in Old World monkey cells
- PMID: 16203999
- PMCID: PMC1239943
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505659102
Cyclophilin A is required for TRIM5{alpha}-mediated resistance to HIV-1 in Old World monkey cells
Abstract
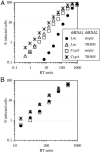
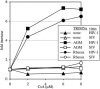
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase cyclophilin A (CypA) embraces an exposed, proline-rich loop on HIV-1 capsid (CA) and renders reverse transcription complexes resistant to an antiviral activity in human cells. A CypA fusion with TRIM5 that is unique to New World owl monkeys also targets HIV-1 CA, but this interaction potently inhibits infection. A similar block to HIV-1 infection in Old World monkeys is attributable to the alpha isoform of the TRIM5 orthologue in these species. To determine whether HIV-1 restriction by Old World monkey TRIM5alpha is modulated by the CA-CypA interaction, RNA interference was used to disrupt CypA in cells from African green monkeys and rhesus macaques. HIV-1 infectivity increased in response to CypA knock-down to the same extent that it increased in response to TRIM5 knock-down. CypA knock-down eliminated the HIV-1 stimulatory effect of cyclosporin A (CsA), a competitive inhibitor of the CypA-CA interaction, or of CA mutants that block binding to CypA but caused no change in titer of retroviruses that don't interact with CypA. Simultaneous knock-down of both CypA and TRIM5 caused minimal additional increase in titer, suggesting that CypA inhibits HIV-1 replication in these cells because it is required for CA recognition by TRIM5alpha. Finally, CsA increased HIV-1 titer in otherwise nonrestrictive feline cells but only after these cells were transduced with Old World monkey TRIM5alpha. Thus, CypA is required for HIV-1 restriction by Old World monkey orthologues of TRIM5alpha.
Figures
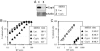


References
-
- Luban, J., Bossolt, K. L., Franke, E. K., Kalpana, G. V. & Goff, S. P. (1993) Cell 73, 1067-1078. - PubMed
-
- Franke, E. K., Yuan, H. E. & Luban, J. (1994) Nature 372, 359-362. - PubMed
-
- Gamble, T. R., Vajdos, F. F., Yoo, S., Worthylake, D. K., Houseweart, M., Sundquist, W. I. & Hill, C. P. (1996) Cell 87, 1285-1294. - PubMed
-
- Thali, M., Bukovsky, A., Kondo, E., Rosenwirth, B., Walsh, C. T., Sodroski, J. & Gottlinger, H. G. (1994) Nature 372, 363-365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

