Global regulation of X chromosomal genes by the MSL complex in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 16204180
- PMCID: PMC1240037
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1343705
Global regulation of X chromosomal genes by the MSL complex in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
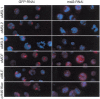
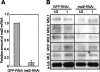
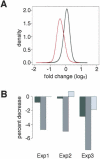
A long-standing model postulates that X-chromosome dosage compensation in Drosophila occurs by twofold up-regulation of the single male X, but previous data cannot exclude an alternative model, in which male autosomes are down-regulated to balance gene expression. To distinguish between the two models, we used RNA interference to deplete Male-Specific Lethal (MSL) complexes from male-like tissue culture cells. We found that expression of many genes from the X chromosome decreased, while expression from the autosomes was largely unchanged. We conclude that the primary role of the MSL complex is to up-regulate the male X chromosome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MSL complex associates with clusters of actively transcribed genes along the Drosophila male X chromosome.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:385-94. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.026. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381321
-
The right dose for every sex.Chromosoma. 2007 Apr;116(2):95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0089-x. Epub 2006 Nov 24. Chromosoma. 2007. PMID: 17124606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PionX sites mark the X chromosome for dosage compensation.Nature. 2016 Sep 8;537(7619):244-248. doi: 10.1038/nature19338. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27580037
-
The Drosophila MSL complex activates the transcription of target genes.Genes Dev. 2005 Oct 1;19(19):2284-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.1343105. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 16204179 Free PMC article.
-
The MSL complex: X chromosome and beyond.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010 Apr;20(2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2010.01.007. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010. PMID: 20167472 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequence signatures involved in targeting the Male-Specific Lethal complex to X-chromosomal genes in Drosophila melanogaster.BMC Genomics. 2012 Mar 19;13:97. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-97. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22424303 Free PMC article.
-
Cumulative contributions of weak DNA determinants to targeting the Drosophila dosage compensation complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(11):3561-72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm282. Epub 2007 May 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17483514 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription rate of noncoding roX1 RNA controls local spreading of the Drosophila MSL chromatin remodeling complex.Mech Dev. 2008 Nov-Dec;125(11-12):1009-19. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.08.003. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Mech Dev. 2008. PMID: 18793722 Free PMC article.
-
Unique transgenic animal model for hereditary hearing loss.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008 Nov;117(11):827-33. doi: 10.1177/000348940811701106. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008. PMID: 19102128 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific pattern formation during early Drosophila development.Genetics. 2013 May;194(1):163-73. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.148205. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23410834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhtar A. and Becker, P.B. 2000. Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 5: 367-375. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw G.J. and Baker, B.S. 1995. The msl-2 dosage compensation gene of Drosophila encodes a putative DNA-binding protein whose expression is sex specifically regulated by Sex-lethal. Development 121: 3245-3258. - PubMed
-
- Belote J.M. and Lucchesi, J.C. 1980a. Control of X chromosome transcription by the maleless gene in Drosophila. Nature 285: 573-575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
