Role of the regulatory gene rirA in the transcriptional response of Sinorhizobium meliloti to iron limitation
- PMID: 16204511
- PMCID: PMC1265945
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.5969-5982.2005
Role of the regulatory gene rirA in the transcriptional response of Sinorhizobium meliloti to iron limitation
Abstract
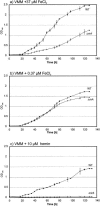
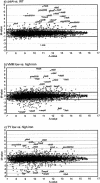
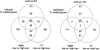
A regulatory network of Sinorhizobium meliloti genes involved in adaptation to iron-limiting conditions and the involvement of the rhizobial iron regulator gene (rirA) were analyzed by mutation and microarray analyses. A constructed S. meliloti rirA mutant exhibited growth defects and enhanced H2O2 sensitivity in the presence of iron, but symbiotic nitrogen fixation was not affected. To identify iron-responsive and RirA-regulated S. meliloti genes, a transcriptome approach using whole-genome microarrays was used. Altogether, 45 genes were found to be jointly derepressed by mutation of rirA and under different iron-limited conditions. As expected, a number of genes involved in iron transport (e.g., hmuPSTU, shmR, rhbABCDEF, rhtX, and rhtA) and also genes with predicted functions in energy metabolism (e.g., fixN3, fixP3, and qxtAB) and exopolysaccharide production (e.g., exoY and exoN) were found in this group of genes. In addition, the iron deficiency response of S. meliloti also involved rirA-independent expression changes, including repression of the S. meliloti flagellar regulon. Finally, the RirA modulon also includes genes that are not iron responsive, including a gene cluster putatively involved in Fe-S cluster formation (sufA, sufS, sufD, sufC, and sufB).
Figures

References
-
- Baichoo, N., T. Wang, R. Ye, and J. D. Helmann. 2002. Global analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Fur regulon and the iron starvation stimulon. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1613-1629. - PubMed
-
- Barnett, M. J., R. F. Fisher, T. Jones, C. Komp, A. P. Abola, F. Barloy-Hubler, L. Bowser, D. Capela, F. Galibert, J. Gouzy, M. Gurjal, A. Hong, L. Huizar, R. W. Hyman, D. Kahn, M. L. Kahn, S. Kalman, D. H. Keating, C. Palm, M. C. Peck, R. Surzycki, D. H. Wells, K. C. Yeh, R. W. Davis, N. A. Federspiel, and S. R. Long. 2001. Nucleotide sequence and predicted functions of the entire Sinorhizobium meliloti pSymA megaplasmid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:9883-9888. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beaumont, H. J., S. I. Lens, W. N. Reijnders, H. V. Westerhoff, and R. J. van Spanning. 2004. Expression of nitrite reductase in Nitrosomonas europaea involves NsrR, a novel nitrite-sensitive transcription repressor. Mol. Microbiol. 54:148-158. - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., H. Berges, E. Krol, C. Bruand, S. Rüberg, D. Capela, E. Lauber, E. Meilhoc, F. Ampe, F. J. de Bruijn, J. Fourment, A. Francez-Charlot, D. Kahn, H. Küster, C. Liebe, A. Pühler, S. Weidner, and J. Batut. 2004. Global changes in gene expression in Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 under microoxic and symbiotic conditions. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 17:292-303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

