Equine and canine Anaplasma phagocytophilum strains isolated on the island of Sardinia (Italy) are phylogenetically related to pathogenic strains from the United States
- PMID: 16204571
- PMCID: PMC1265917
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.6418-6422.2005
Equine and canine Anaplasma phagocytophilum strains isolated on the island of Sardinia (Italy) are phylogenetically related to pathogenic strains from the United States
Abstract
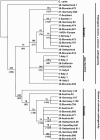
The presence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, a tick-transmitted zoonotic pathogen, was investigated in Sardinia using a molecular approach. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that Sardinian strains are genetically distinct from the two lineages previously described in Europe and are closely related to strains isolated in different areas of the United States.
Figures

References
-
- Aguero-Rosenfeld, M. E., H. W. Horovitz, G. P. Wormser, D. F. Mc-Kenna, J. Nowakowski, J. Munoz, and J. S. Dumler. 1996. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis: a case series from a medical center in New York State. Ann. Intern. Med. 125:904-908. - PubMed
-
- Alekseev, A. N., H. V. Dubinina, A. V. Semenov, and C. V. Bolshakov. 2001. Evidence of ehrlichiosis agents found in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from migratory birds. J. Med. Entomol. 38:471-474. - PubMed
-
- Blanco, J. R., and J. A. Oteo. 2002. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 8:763-772. - PubMed
-
- Dumler, J. S., A. F. Barbet, C. P. J. Bekker, G. A. Dasch, G. H. Palmer, S. C. Ray, Y. Rikihisa, and F. R. Rurangirwa. 2001. Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia, and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and ‘HGE agent’ as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:2145-2165. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

