Protective effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on bone destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 16207319
- PMCID: PMC1257432
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1779
Protective effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on bone destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
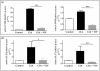
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease of unknown etiology, characterized by the presence of inflammatory synovitis accompanied by destruction of joint cartilage and bone. Treatment with vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) prevents experimental arthritis in animal models by downregulation of both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease. The aim of this study was to characterize the protective effect of VIP on bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice. We have studied the expression of different mediators implicated in bone homeostasis, such as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK), receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL), osteoprotegerin (OPG), IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-11 and IL-17. Circulating cytokine levels were assessed by ELISA and the local expression of mediators were determined by RT-PCR in mRNA extracts from joints. VIP treatment resulted in decreased levels of circulating IL-6, IL-1beta and TNFalpha, and increased levels of IL-4 and IL-10. CIA-mice treated with VIP presented a decrease in mRNA expression of IL-17, IL-11 in the joints. The ratio of RANKL to OPG decreased drastically in the joint after VIP treatment, which correlated with an increase in levels of circulating OPG in CIA mice treated with VIP. In addition, VIP treatment decreased the expression of mRNA for RANK, iNOS and COX-2. To investigate the molecular mechanisms involved, we tested the activity of NFkappaB and AP-1, two transcriptional factors closely related to joint erosion, by EMSA in synovial cells from CIA mice. VIP treatment in vivo was able to affect the transcriptional activity of both factors. Our data indicate that VIP is a viable candidate for the development of treatments for RA.
Figures



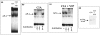
References
-
- Takayanagi H, Iizuka H, Juji T, Nakagawa T, Yamamoto A, Myazaki T, Koshihara Y, Oda H, Nakamura K, Tanaka S. Involvement of receptor activator of nuclear factor kB ligand/osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis from synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:259–269. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<259::AID-ANR4>3.0.CO;2-W. - DOI - PubMed
-
- O'Gradaigh D, Ireland D, Bord S, Compston JE. Joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: interactions between tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 1, and receptor activator of nuclear factor kB ligand (RANKL) regulate osteoclasts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:354–359. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.008458. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

