Searching for differentially expressed gene combinations
- PMID: 16207359
- PMCID: PMC1257471
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-10-r88
Searching for differentially expressed gene combinations
Abstract
We propose 'CorScor', a novel approach for identifying gene pairs with joint differential expression. This is defined as a situation with good phenotype discrimination in the bivariate, but not in the two marginal distributions. CorScor can be used to detect phenotype-related dependencies and interactions among genes. Our easily interpretable approach is scalable to current microarray dimensions and yields promising results on several cancer-gene-expression datasets.
Figures
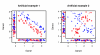
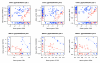

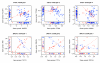
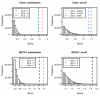
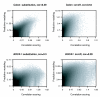
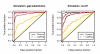
References
-
- Efron B, Tibshirani R, Storey J, Tusher V. Empirical Bayes analysis of a microarray experiment. J Am Stat Assoc. 2001;96:1151–1160. doi: 10.1198/016214501753382129. - DOI
-
- Dudoit S, Fridlyand J. Classification in microarray experiments. In: Speed T, editor. Statistical Analysis of Gene Expression Data. New York: Chapman and Hall; 2003. pp. 93–158.
-
- Dettling M, Bühlmann P. Finding predictive gene groups from microarray data. J Multivariate Anal. 2004;90:106–131. doi: 10.1016/j.jmva.2004.02.012. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

