Inferring protein domain interactions from databases of interacting proteins
- PMID: 16207360
- PMCID: PMC1257472
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-10-r89
Inferring protein domain interactions from databases of interacting proteins
Abstract
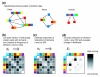
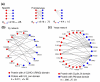
We describe domain pair exclusion analysis (DPEA), a method for inferring domain interactions from databases of interacting proteins. DPEA features a log odds score, Eij, reflecting confidence that domains i and j interact. We analyzed 177,233 potential domain interactions underlying 26,032 protein interactions. In total, 3,005 high-confidence domain interactions were inferred, and were evaluated using known domain interactions in the Protein Data Bank. DPEA may prove useful in guiding experiment-based discovery of previously unrecognized domain interactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DAPID: a 3D-domain annotated protein-protein interaction database.Genome Inform. 2006;17(2):206-15. Genome Inform. 2006. PMID: 17503393
-
Understanding protein-protein interactions using local structural features.J Mol Biol. 2013 Apr 12;425(7):1210-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.01.014. Epub 2013 Jan 23. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23353828
-
Co-evolutionary analysis of domains in interacting proteins reveals insights into domain-domain interactions mediating protein-protein interactions.J Mol Biol. 2006 Sep 29;362(4):861-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.072. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16949097 Free PMC article.
-
GTPase-activating proteins for heterotrimeric G proteins: regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) and RGS-like proteins.Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:795-827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.795. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10966476 Review.
-
Protein modules and protein-protein interaction. Introduction.Adv Protein Chem. 2002;61:1-8. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(02)61000-9. Adv Protein Chem. 2002. PMID: 12461819 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Recovering protein-protein and domain-domain interactions from aggregation of IP-MS proteomics of coregulator complexes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002319. Epub 2011 Dec 29. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 22219718 Free PMC article.
-
A domain-based approach to predict protein-protein interactions.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Jun 13;8:199. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-199. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17567909 Free PMC article.
-
A Proteome-wide Fission Yeast Interactome Reveals Network Evolution Principles from Yeasts to Human.Cell. 2016 Jan 14;164(1-2):310-323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.037. Cell. 2016. PMID: 26771498 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-level learning: improving the prediction of protein, domain and residue interactions by allowing information flow between levels.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Aug 5;10:241. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-241. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19656385 Free PMC article.
-
PPIDomainMiner: Inferring domain-domain interactions from multiple sources of protein-protein interactions.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Aug 9;17(8):e1008844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008844. eCollection 2021 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34370723 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

