Comparison of three molecular methods used for subtyping of Legionella pneumophila strains isolated during an epidemic of Legionellosis in Rome
- PMID: 16208015
- PMCID: PMC1248497
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.10.5348-4350.2005
Comparison of three molecular methods used for subtyping of Legionella pneumophila strains isolated during an epidemic of Legionellosis in Rome
Abstract
In the summer of 2003 a community-acquired outbreak of Legionella pneumophila occurred in Rome, Italy. Three molecular typing methods, pulse-field gel electrophoresis, amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis, and sequence-based typing (SBT), were used to establish the clonal correlation among the isolates of the epidemic cluster. By comparison of the methods, SBT was the most rapid and the easiest to perform and provided unambiguous results.
Figures
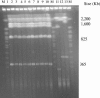
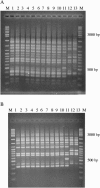
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 1994. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley Interscience, New York, N.Y.
-
- Bartlett, J. G. 1993. Legionnaires' disease: over-treated, under-diagnosed. J. Crit. Illness 8:755-768.
-
- Bernarder, S., K. Jacobson, H. Helbig, P. C. Luck, and M. Lundholm. 2003. A hospital-associated outbreak of Legionnaires' disease caused by Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 is characterized by stable genetic fingerprinting but variable monoclonal antibody patterns. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:2503-2508. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castellani Pastoris, M., L. Ciceroni, R. Lo Monaco, P. Goldoni, B. Mentore, G. Flego, L. Cattani, S. Ciarrocchi, A. Pinto, and P. Visca. 1997. Molecular epidemiology of an outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a cooling tower in Genova-Sestri Ponente, Italy. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 16:883-892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

