Fatal pulmonary infection associated with a novel organism, "para-streptomyces abscessus"
- PMID: 16208023
- PMCID: PMC1248464
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.10.5376-5379.2005
Fatal pulmonary infection associated with a novel organism, "para-streptomyces abscessus"
Abstract
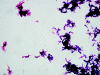
Actinomycetes are increasingly recognized as pathogenic in the immunocompromised host. We isolated an asporogenous, nonmotile, aerobic gram-positive rod from a transplant recipient with a fatal pulmonary infection. The pathology was similar to that associated with Rhodococcus equi, including intra-histiocytic localization. The organism was relatively inert in standard biochemical tests. 16S rRNA gene sequencing indicated a potentially unique organism most closely related to the genus Streptomyces, for which we propose the name "Para-streptomyces abscessus."
Figures


Similar articles
-
Grouping of streptomycetes using 16S-ITS RFLP fingerprinting.Res Microbiol. 2005 Jun-Jul;156(5-6):755-62. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2005.01.017. Epub 2005 Feb 26. Res Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15950131
-
Streptacidiphilus jiangxiensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from acidic rhizosphere soil in China.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2004 Aug;86(2):159-65. doi: 10.1023/B:ANTO.0000036124.18820.ae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2004. PMID: 15280649
-
First case of Pseudoclavibacter bifida bacteremia in an immunocompromised host with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Jun;51(6):1973-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00138-13. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23536403 Free PMC article.
-
Genus Kitasatospora, taxonomic features and diversity of secondary metabolites.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017 May;70(5):506-513. doi: 10.1038/ja.2017.8. Epub 2017 Feb 15. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 28196972 Review.
-
Current taxonomy of Rhodococcus species and their role in infections.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Nov;37(11):2045-2062. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3364-x. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30159693 Review.
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Balows, A., W. J. Hausler, Jr., K. L. Herrman, H. D. Isenberg, D. Henry, and H. J. Shadomy (ed.). 1991. Manual of clinical microbiology, 5th ed., p. 350-352. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
-
- Brown, J. M., M. M. McNeil, and E. P. Desmond. 1999. Nocardia, Rhodococcus, Gordona, Actinomadura, Streptomyces, and other actinomyces of medical importance, p. 389. In P. R. Murray, E. J. Baron, M. A. Pfaller, F. C. Tenover, and R. H. Yolken (ed.), Manual of clinical microbiology, 7th ed. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
-
- Reference deleted.
-
- Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783-791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

