Activation of focal adhesion kinase enhances the adhesion and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells via extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 signaling pathway activation
- PMID: 16209712
- PMCID: PMC1266395
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-4-37
Activation of focal adhesion kinase enhances the adhesion and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells via extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 signaling pathway activation
Abstract
Background: Interaction with integrin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) regulates the cancer cell adhesion and invasion into extracellular matrix (ECM). In addition, phosphorylation of FAK correlates with the increase of cell motility and invasion. Adhesion and spreading of cancer cells on a variety of ECM proteins, including collagen type IV (Coll IV), leads to an increase in tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of FAK. In this study, we investigated the mechanism of activation of FAK and its downstream extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-1/2 signaling following stimulation by interleukin (IL)-1alpha and adhesion to ECM with subsequent enhancement of pancreatic cancer cell adhesion and invasion.
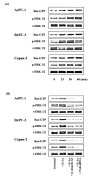
Results: In immunoblotting analysis, all three pancreatic cancer cell lines (AsPC-1, BxPC-3, and Capan-2) expressed the protein of FAK and beta1 integrin. Enhancement of FAK protein association with beta1 integrin when cells were plated on Coll IV was more increased by stimulation with IL-1alpha. Preincubation with anti-beta1 integrin antibody and FAK siRNA transfection inhibited the association of FAK with beta1 integrin of pancreatic cancer cells. FAK phosphorylation was observed by adhesion to Coll IV, furthermore, stronger FAK phosphorylation was observed by stimulation with IL-1alpha of pancreatic cancer cells adhered to Coll IV in time-dependent manner. Genistein, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, markedly inhibited the FAK phosphorylation. IL-1alpha stimulation and Coll IV adhesion enhanced the activation of Ras, as evidenced by the increased Ras-GTP levels in pancreatic cancer cells. Activation of Ras correlated with the phosphorylation of ERK. While not statistical affecting the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells, IL-1alpha-induced adhesion and invasion on Coll IV were inhibited with FAK gene silencing by siRNA, beta1 integrin blocking, and inhibition of FAK phosphorylation. PD98059, a MEK inhibitor, also inhibited IL-1alpha-induced enhancement of adhesion and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that activation of FAK is involved with the aggressive capability in pancreatic cancer through Ras/ERK signaling pathway. Based on our results, we suggest that the modification of IL-1, FAK, and integrins functions might be a novel therapeutic approach to aggressive spread of pancreatic cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Recruitment of focal adhesion kinase and paxillin to beta1 integrin promotes cancer cell migration via mitogen activated protein kinase activation.BMC Cancer. 2004 May 7;4:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-4-18. BMC Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15132756 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of focal adhesion kinase in human lung cancer cells involves multiple and potentially parallel signaling events.J Cell Mol Med. 2005 Apr-Jun;9(2):387-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2005.tb00364.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15963258 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-dependent protein tyrosine phosphorylation is a key regulatory event in collagen-IV-mediated adhesion and proliferation of human lung tumor cell line, Calu-1.Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 Aug;78(2):450-7. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.01.042. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15276495
-
Focal adhesion kinase and its potential involvement in tumor invasion and metastasis.Head Neck. 1998 Dec;20(8):745-52. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0347(199812)20:8<745::aid-hed14>3.0.co;2-z. Head Neck. 1998. PMID: 9790298 Review.
-
Focal adhesion kinase signaling in unexpected places.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;45:24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.01.003. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28213315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of elevated glucose levels on interactions of cardiac fibroblasts with the extracellular matrix.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2007 Sep-Oct;43(8-9):297-305. doi: 10.1007/s11626-007-9052-2. Epub 2007 Sep 12. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2007. PMID: 17849168
-
Hydro-Seq enables contamination-free high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing for circulating tumor cells.Nat Commun. 2019 May 15;10(1):2163. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10122-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31092822 Free PMC article.
-
Causal inference of gene regulation with subnetwork assembly from genetical genomics data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Mar;42(5):2803-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1277. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24322297 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of prognosis-associated genes in pancreatic tumor metastasis: lessons from global studies in bioinformatics.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021 Sep;40(3):721-738. doi: 10.1007/s10555-021-09991-1. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021. PMID: 34591244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 via the molecular cross-talk between the mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein kinase Cdelta pathways in human adult articular chondrocytes.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 13;282(15):11110-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609040200. Epub 2007 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17311929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmitz KJ, Grabellus F, Callies R, Otterbach F, Wohlschlaeger J, Levkau B, Kimmig R, Schmid KW, Baba HA. High expression of focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) in node-negative breast cancer is related to overexpression of HER-2/neu and activated Akt kinase but does not predict outcome. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7:R194–R203. doi: 10.1186/bcr977. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

