A TRAIL receptor-dependent synthetic lethal relationship between MYC activation and GSK3beta/FBW7 loss of function
- PMID: 16210249
- PMCID: PMC1257707
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505114102
A TRAIL receptor-dependent synthetic lethal relationship between MYC activation and GSK3beta/FBW7 loss of function
Abstract
The MYC protooncogene is frequently deregulated in human cancers. Here, by screening a kinase-directed library of small inhibitory RNAs, we identify glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) as a gene whose inactivation potentiates TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand death receptor-mediated apoptosis specifically in MYC-overexpressing cells. Small inhibitory RNA-induced silencing of GSK3beta prevents phosphorylation of MYC on T58, thereby inhibiting recognition of MYC by the E3 ubiquitin ligase component FBW7. Attenuating the GSK3beta-FBW7 axis results in stabilization of MYC, up-regulation of surface levels of the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand death receptor 5, and potentiation of death receptor 5-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. These results identify GSK3beta and FBW7 as potential cancer therapeutic targets and MYC as a critical substrate in the GSK3beta survival-signaling pathway. The results also demonstrate paradoxically that MYC-expressing tumors might be treatable by drug combinations that increase rather than decrease MYC oncoprotein function.
Figures

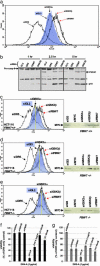
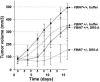
Similar articles
-
The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 15;101(24):9085-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402770101. Epub 2004 May 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15150404 Free PMC article.
-
Fbw7 promotes ubiquitin-dependent degradation of c-Myb: involvement of GSK3-mediated phosphorylation of Thr-572 in mouse c-Myb.Oncogene. 2009 Jun 25;28(25):2393-405. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.111. Epub 2009 May 4. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19421138
-
The v-Jun point mutation allows c-Jun to escape GSK3-dependent recognition and destruction by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase.Cancer Cell. 2005 Jul;8(1):25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.06.005. Cancer Cell. 2005. PMID: 16023596
-
Myc tagging along the TRAIL to death receptor 5.Cell Cycle. 2004 Jul;3(7):920-2. Epub 2004 Jul 8. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15254425 Review.
-
[Function and mechanism of tumor suppressor gene FBW7 in tumorigenesis].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Mar;42(3):214-6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2013.03.020. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23769449 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
SGO1 is involved in the DNA damage response in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 19;6:31615. doi: 10.1038/srep31615. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27539729 Free PMC article.
-
Small interfering RNA-based molecular therapy of cancers.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Sep;32(9):488-93. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10280. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23327796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of unique sensitizing targets for anti-inflammatory CDDO-Me in metastatic melanoma by a large-scale synthetic lethal RNAi screening.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 Jan;26(1):97-112. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12031. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23020131 Free PMC article.
-
Celecoxib promotes c-FLIP degradation through Akt-independent inhibition of GSK3.Cancer Res. 2011 Oct 1;71(19):6270-81. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0838. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21868755 Free PMC article.
-
Domain-specific c-Myc ubiquitylation controls c-Myc transcriptional and apoptotic activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 15;110(3):978-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208334110. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23277542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luscher, B. (2001) Gene 277, 1-14. - PubMed
-
- Oster, S. K., Ho, C. S., Soucie, E. L. & Penn, L. Z. (2002) Adv. Cancer Res. 84, 81-154. - PubMed
-
- Evan, G. I., Wyllie, A. H., Gilbert, C. S., Littlewood, T. D., Land, H., Brooks, M., Waters, C. M., Penn, L. Z. & Hancock, D. C. (1992) Cell 119-128. - PubMed
-
- Pelengaris, S., Khan, M. & Evan, G. (2002) Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 764-776. - PubMed
-
- Wang, Y., Engels, I. H., Knee, D. A., Nasoff, M., Deveraux, Q. L. & Quon, K. C. (2004) Cancer Cell. 5, 501-512. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

