Osmotic demyelination syndrome
- PMID: 16210283
- PMCID: PMC1246086
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.331.7520.829
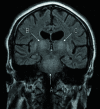
Osmotic demyelination syndrome
Figures

References
-
- Liamis GL, Milionis HJ, Rizos EC, Siamopoulos KC, Elisaf MS. Mechanisms of hyponatraemia in alcohol patients. Alcohol Alcohol 2000;35: 612-6. - PubMed
-
- Adrogue HJ, Madias NE. Hyponatraemia. N Engl J Med 2000;342: 1581-9. - PubMed
-
- Brown WD. Osmotic demyelination disorders: central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Curr Opin Neurol 2000;13: 691-7. - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson BE, Pierides AM, Bradley WG. Central pontine myelinolysis: two cases with associated electrolyte disturbance. Q J Med 1976;45: 373-86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
