Structure and mechanisms of the proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzyme USP14
- PMID: 16211010
- PMCID: PMC1276716
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600832
Structure and mechanisms of the proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzyme USP14
Abstract
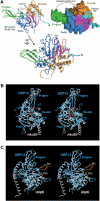
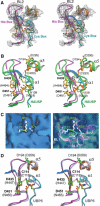
The ubiquitin-specific processing protease (UBP) family of deubiquitinating enzymes plays an essential role in numerous cellular processes. Mammalian USP14 (Ubp6 in yeast) is unique among known UBP enzymes in that it is activated catalytically upon specific association with the 26S proteasome. Here, we report the crystal structures of the 45-kDa catalytic domain of USP14 in isolation and in a complex with ubiquitin aldehyde, which reveal distinct structural features. In the absence of ubiquitin binding, the catalytic cleft leading to the active site of USP14 is blocked by two surface loops. Binding by ubiquitin induces a significant conformational change that translocates the two surface loops thereby allowing access of the ubiquitin C-terminus to the active site. These structural observations, in conjunction with biochemical characterization, identify important regulatory mechanisms for USP14.
Figures



References
-
- Amerik AY, Hochstrasser M (2004) Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695: 189–207 - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, Delano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS (1998) Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D 54: 905–921 - PubMed
-
- Chernova TA, Allen KD, Wesoloski LM, Shanks JR, Chernoff YO, Wilkinson KD (2003) Pleiotropic effects of Ubp6 loss on drug sensitivities and yeast prion are due to depletion of the free ubiquitin pool. J Biol Chem 278: 52102–52115 - PubMed
-
- Chung KK, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2001) The role of the ubiquitin–proteasomal pathway in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 24: S7–S14 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

