Antibody-mediated rejection in human cardiac allografts: evaluation of immunoglobulins and complement activation products C4d and C3d as markers
- PMID: 16212640
- PMCID: PMC1363343
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01074.x
Antibody-mediated rejection in human cardiac allografts: evaluation of immunoglobulins and complement activation products C4d and C3d as markers
Abstract
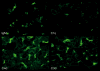
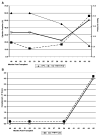
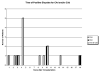
Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) in human heart transplantation is an immunopathologic process in which injury to the graft is in part the result of activation of complement and it is poorly responsive to conventional therapy. We evaluated by immunofluorescence (IF), 665 consecutive endomyocardial biopsies from 165 patients for deposits of immunoglobulins and complement. Diffuse IF deposits in a linear capillary pattern greater than 2+ were considered significant. Clinical evidence of graft dysfunction was correlated with complement deposits. IF 2+ or higher was positive for IgG, 66%; IgM, 12%; IgA, 0.6%; C1q, 1.8%; C4d, 9% and C3d, 10%. In 3% of patients, concomitant C4d and C3d correlated with graft dysfunction or heart failure. In these 5 patients AMR occurred 56-163 months after transplantation, and they responded well to therapy for AMR but not to treatment with steroids. Systematic evaluation of endomyocardial biopsies is not improved by the use of antibodies for immunoglobulins or C1q. Concomitant use of C4d and C3d is very useful to diagnose AMR, when correlated with clinical parameters of graft function. AMR in heart transplant patients can occur many months or years after transplant.
Figures
References
-
- Baldwin WM, III, Halloran PF. Antibody-mediated rejection. In: Racusen LC, Solez K, Burdick JF, editors. Kidney transplant rejection. Marcel Decker; New York: 1998. pp. 127–147.
-
- Billingham ME, Cary NR, Hammond ME, et al. Heart Rejection Study Group The International Society for Heart Transplantation A working formulation for the standardization of nomenclature in the diagnosis of heart and lung rejection. J Heart Transplant. 1990;9:587–593. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez ER. The pathology of heart transplant biopsy specimens: revisiting the 1990 ISHLT working formulation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2003;22:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Lones MA, Czer LS, Trento A, Harasty D, Miller JM, Fishbein MC. Clinical-pathologic features of humoral rejection in cardiac allografts: a study in 81 consecutive patients. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1995;14(1 Pt 1):151–162. - PubMed
-
- Michaels PJ, Espejo ML, Kobashigawa J, et al. Humoral rejection in cardiac transplantation: risk factors, hemodynamic consequences and relationship to transplant coronary artery disease. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2003;22:58–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

