Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis
- PMID: 16212809
- PMCID: PMC1871724
- DOI: 10.1215/S1152851705000050
Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis
Abstract
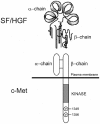
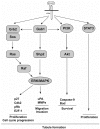
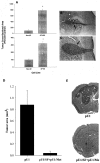
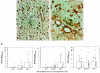
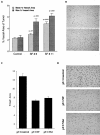
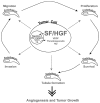
The multifunctional growth factor scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor (SF/HGF) and its receptor tyrosine kinase c-Met have emerged as key determinants of brain tumor growth and angiogenesis. SF/HGF and c-Met are expressed in brain tumors, the expression levels frequently correlating with tumor grade, tumor blood vessel density, and poor prognosis. Overexpression of SF/HGF and/or c-Met in brain tumor cells enhances their tumorigenicity, tumor growth, and tumor-associated angiogenesis. Conversely, inhibition of SF/HGF and c-Met in experimental tumor xenografts leads to inhibition of tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis. SF/HGF is expressed and secreted mainly by tumor cells and acts on c-Met receptors that are expressed in tumor cells and vascular endothelial cells. Activation of c-Met leads to induction of proliferation, migration, and invasion and to inhibition of apoptosis in tumor cells as well as in tumor vascular endothelial cells. Activation of tumor endothelial c-Met also induces extracellular matrix degradation, tubule formation, and angiogenesis in vivo. SF/HGF induces brain tumor angiogenesis directly through only partly known mechanisms and indirectly by regulating other angiogenic pathways such as VEGF. Different approaches to inhibiting SF/HGF and c-Met have been recently developed. These include receptor antagonism with SF/HGF fragments such as NK4, SF/HGF, and c-Met expression inhibition with U1snRNA/ribozymes; competitive ligand binding with soluble Met receptors; neutralizing antibodies to SF/HGF; and small molecular tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Use of these inhibitors in experimental tumor models leads to inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis. In this review, we summarize current knowledge of how the SF/HGF:c-Met pathway contributes to brain tumor malignancy with a focus on glioma angiogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Abounader R, Ranganathan S, Lal B, Fielding K, Book A, Dietz H, Burger P, Laterra J. Reversion of human glioblastoma malignancy by U1 small nuclear RNA/ribozyme targeting of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor and c-met expression. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91:1548–1556. - PubMed
-
- Abounader R, Lal B, Luddy C, Koe G, Davidson B, Rosen EM, Laterra J. In vivo targeting of SF/HGF and c-met expression via U1snRNA/ribozymes inhibits glioma growth and angiogenesis and promotes apoptosis. FASEB J. 2002;16:108–110. - PubMed
-
- Abounader R, Reznik T, Kuchner E, Kwon S, Saldanha U, Dasgupta N, Russel J, Eberhart C, Laterra J. Characterization of the scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor: c-Met pathway in human medulloblastoma malignancy. Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2004a Available at http://aacr04.agora.com/planner (abstract 4348) - PubMed
-
- Abounader R, Montgomery R, Dietz H, Laterra J. Design and expression of chimeric U1/ribozyme transgenes. Methods Mol Biol. 2004b;252:209–219. - PubMed
-
- Alexandrakis MG, Passam FJ, Ganotakis E, Dafnis E, Dambaki C, Konsolas J, Kyriakou DS, Stathopoulos E. Bone marrow microvascular density and angiogenic growth factors in multiple myeloma. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2004;42:1122–1126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

